Contents
- 1 Viral Hepatitis B Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How To Distinguish Viral Hepatitis B from Other Conditions
- 2.1 Distinguish Hepatitis A from Viral Hepatitis B – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Hepatitis C from Viral Hepatitis B – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Infectious Mononucleosis from Viral Hepatitis B – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish Liver Carcinoma from Viral Hepatitis B – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Hepatitis D from Viral Hepatitis B – Diagnosis
- 3 Important Red Flags in Viral Hepatitis B
Viral Hepatitis B Differential Diagnosis Table:
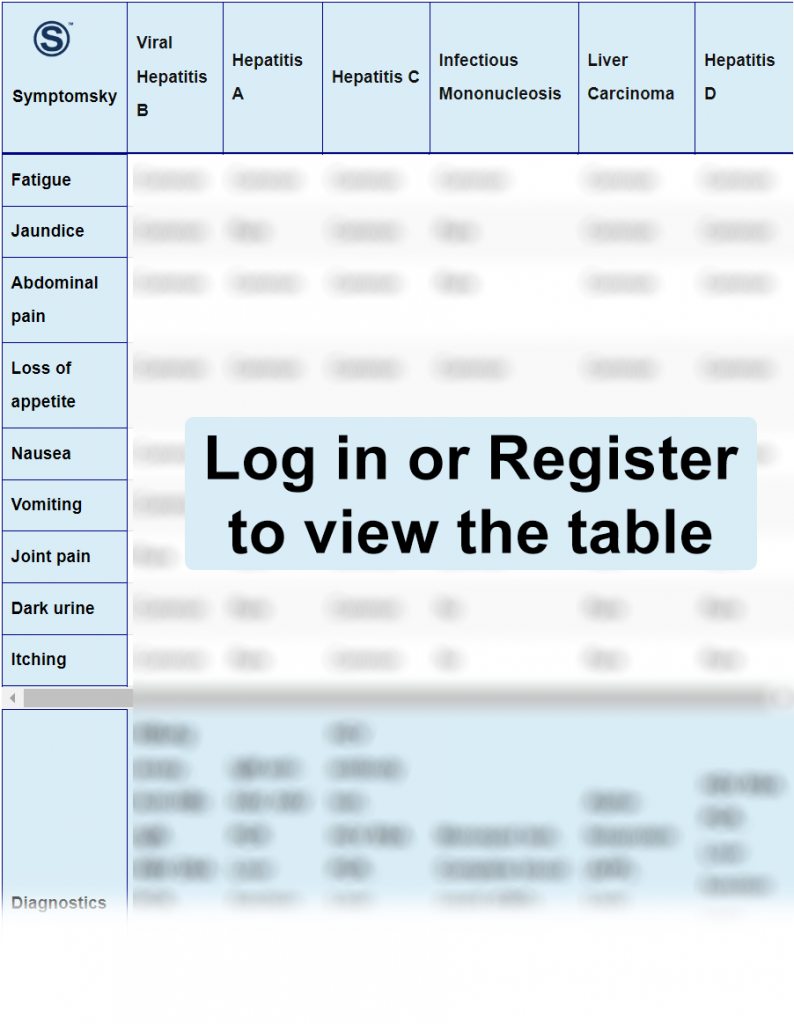
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that causes inflammation and sometimes damage to the liver. In most cases, hepatitis B is an acute infection that resolves within a few months, but in some patients, it can lead to chronic disease and severe liver damage.
Hepatitis B is transmitted from one person to another through body fluids, either from blood transmission or sexual intercourse. Pregnant women with hepatitis B can transmit the virus to their baby as well.
Serology tests are the main diagnostic test for hepatitis B. IgM and IgG can detect past or recent infection of the disease. Positive HBsAg and HBV DNA indicate current infection and replication of the virus.
Treatment of hepatitis B varies according to many factors. If the patient just got exposed, an immunoglobulin shot may be all that is needed. In acute infection, symptomatic treatment is given until resolution of symptoms, and in chronic infection, treatment can start from antiviral medication to liver transplantation.
How To Distinguish Viral Hepatitis B from Other Conditions
Distinguish Hepatitis A from Viral Hepatitis B – Diagnosis
Hepatitis A is a viral infection that affects the liver. It usually transmitted through contaminated food or water. Hepatitis A is usually a mild infection that resolves on its own and it can be asymptomatic, but in some rare cases, it can lead to acute liver failure and death. Once the patient is infected with hepatitis A, they have immunity for life.
- Serology test to detect presence of HAV antibodies like IgM and IgG.
- RT-PCR is the confirmative test. It can help in detecting viral RNA and indicate current infection.
- Some blood tests like liver function tests and bilirubin levels can help in monitoring disease prognosis and extent of damage.
Distinguish Hepatitis C from Viral Hepatitis B – Diagnosis
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that causes inflammation and damage to the liver. It can transmit through blood transfusion and unprotected sex. Hepatitis C is the leading cause for liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. A few years ago, the disease was chronic with no available treatment but recently antiviral medication led to complete cure from the disease.
- HCV RNA detection by RT PCR is the main diagnostic test for detection of current infection of hepatitis C.
- Serology testing can be used in initial investigation, to check presence of antibodies.
- Liver function tests may be needed to know prognosis of disease and extent of liver damage.
- Rarely, in late stages, a liver biopsy may be needed to rule out liver malignancy.
Distinguish Infectious Mononucleosis from Viral Hepatitis B – Diagnosis
Infectious mononucleosis commonly known as mono, is a viral infection caused by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and cytomegalovirus (CMV). The disease is transmitted by transmission of saliva. Although the disease itself is not dangerous, sometimes it can cause enlarged spleen that may last even after recovery.
- Initial diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis is mainly based on clinical presentation and clinical history.
- Rapid mono test is usually the main diagnostic tool for diagnosis of the disease.
- Serology tests against EBV and CMV for detection of antibodies help in diagnosis.
“Rarely, mono can cause liver damage with symptoms of jaundice. Most patients with mono and liver involvement have abnormal liver function.”
Distinguish Liver Carcinoma from Viral Hepatitis B – Diagnosis
Liver carcinoma is the cancer of the liver. It’s one of the most aggressive tumors. It has many types but the most common is hepatocellular carcinoma. A lot of reasons can cause liver cancer, mainly hepatitis C and alcohol. Most people don’t recognize liver cancer except in late stages, that’s why its survival rate is low.
- Liver biopsy is the main diagnostic test for liver carcinoma. It’s the confirmative test and can detect cancer type.
- Imaging tests like MRI, CT, and PET-scan can help to see the extent of liver damage and if cancer has metastasized to other organs.
- Some tumor markers like Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) can help in initial investigation but it’s not a confirmative test.
Distinguish Hepatitis D from Viral Hepatitis B – Diagnosis
Hepatitis D is an inflammation in the liver caused by virus. It’s also called delta hepatitis, but hepatitis D only occurs as a co-infection with hepatitis B, this can lead to a very aggressive chronic form of inflammation in the liver.
- Serology tests for detecting IgM and IgG of virus.
- RT-PCR for detection of virus RNA is the confirmative test.
- Routine liver function test is needed to monitor extent of liver damage and prognosis of disease and treatment response.
“Co-infection of Hepatitis D with Hepatitis B accelerates disease leading to progression of liver damage to liver cirrhosis and liver carcinoma.”
Important Red Flags in Viral Hepatitis B
Although Hepatitis B can lead to progressive damage in the liver, vaccines are now available which helped in decrease in disease occurrence. The disease itself has no current cure but it usually goes away by itself in few months.
Hepatitis B can be a chronic disease in some patients and lead to extensive damage in the liver. Some red flag symptoms may present that patients need to know that may indicate liver damage or poor prognosis of disease.
Hematemesis or GIT bleeding with marked increase in bleeding profile may indicate presence of liver cirrhosis.
Altered conscious level and confusion require immediate medical emergency because it may reflect hepatic decompensation.
Co-infection with hepatitis D as mentioned above is a red flag itself, since it worsens disease and decreases response of treatment.
