Contents
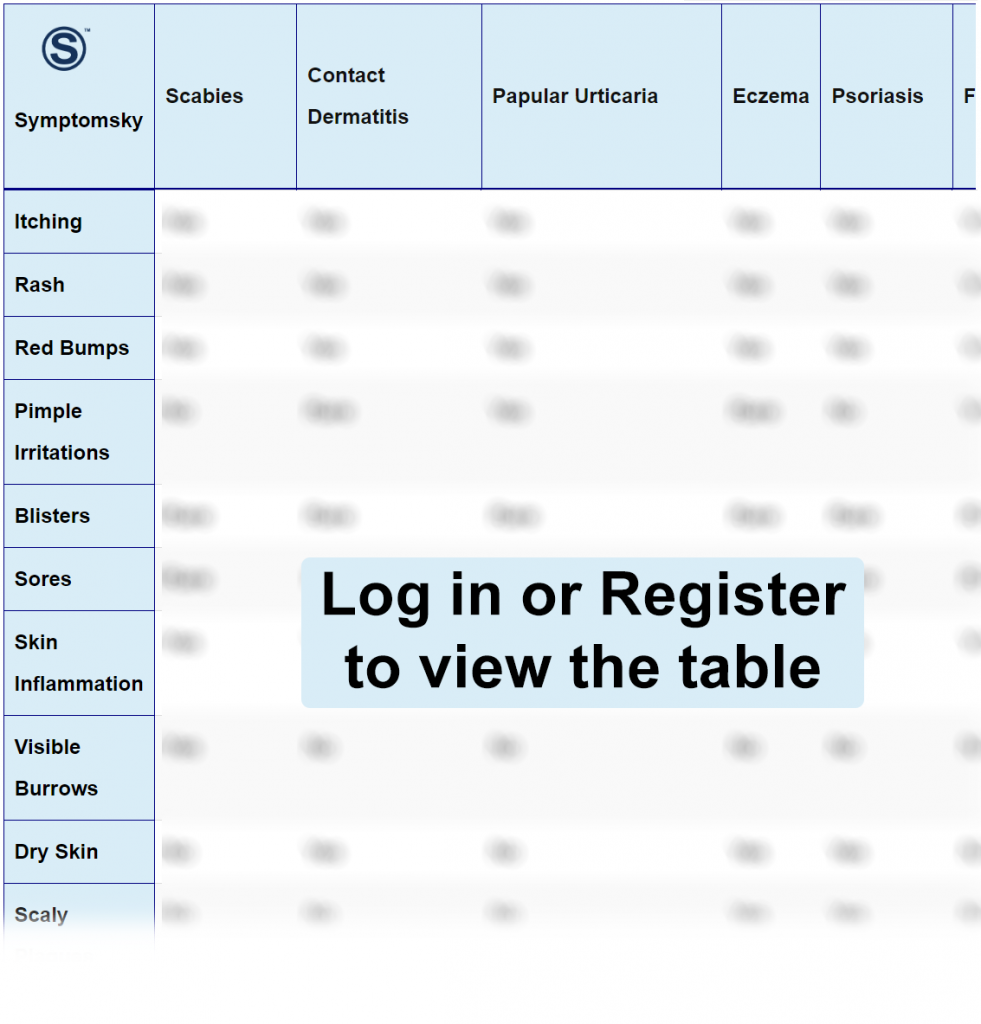
- 1 Scabies Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How To Differentiate Scabies from Other Diseases
- 2.1 Distinguish Contact Dermatitis from Scabies – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Papular Urticaria from Scabies – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Eczema from Scabies – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish Psoriaris from Scabies – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Folliculitis from Scabies – Diagnosis
- 2.6 Distinguish Prurigo Nodularis from Scabies – Diagnosis
- 2.7 Distinguish Dermatitis Herpetiformis from Scabies – Diagnosis
- 2.8 Distinguish Erythema Multiforme from Scabies – Diagnosis
- 2.9 Distinguish Pediculosis from Scabies – Diagnosis
- 2.10 Distinguish Drug Eruptions from Scabies – Diagnosis
- 3 Important Red Flags with Scabies
Scabies Differential Diagnosis Table:
Scabies is a parasitic infection caused by a host-specific mite, Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis, that burrows into the skin and lays eggs, causing intense itching and a rash. It can spread very fast through person-to-person contact since it is highly contagious. Scabies is mainly common in hot tropical countries and highly crowded places.
Scabies symptoms normally start manifesting 4-6 weeks after contamination. Some of the symptoms include severe itch which worsens at night, itchy lines and bumps on the fingers, wrists, arms, legs, and area of the belt, inflamed bumps on male genitalia, and female breasts. They normally appear as serpiginous, grayish, threadlike elevations in the superficial epidermis, ranging from 2-20mm long.
Some of the most burrowed locations include the webbed spaces of the finger, flexor surfaces of the wrist, elbows, axillae, belt line, feet, scrotum in males, and areolae in females. Diagnosis is usually confirmed by light microscopic identification of mites, larvae, ova, or scybala in skin scrapings. Management of scabies includes administration of scabicidal agents like ivermectin, lindane, or permethrin. One can also administer an antimicrobial agent if a secondary infection has developed.
How To Differentiate Scabies from Other Diseases
Distinguish Contact Dermatitis from Scabies – Diagnosis
This is an irritation or rash on the skin which develops when one comes in contact with an allergen. Usually a reaction. Types include allergic contact dermatitis and irritant contact dermatitis.
- Scabies spread through contact since it is highly contagious while contact dermatitis cannot be transmitted since it’s a reaction to an allergen.
- Scabies is a parasitic infection while contact dermatitis is an allergen-triggered reaction.
- Scabies rash is mainly found in body folds while contact dermatitis rash is found in the site of contact with allergen.
- Patch testing can be used to differentiate.
Distinguish Papular Urticaria from Scabies – Diagnosis
This is a common papulovesicular reaction manifested by chronic or recurrent papules caused by a hypersensitivity reaction to bites of mosquitoes, fleas, bed bugs, and other insects.
- Scabies rash presents with burrow tracks for the mites while papular urticaria generally presents with bumps.
- Immunohistochemical analysis reveals abundant T lymphocytes and macrophages in papular urticaria.
- Histopathology can be used to differentiate.
Distinguish Eczema from Scabies – Diagnosis
Also called atopic dermatitis. This is an inflammatory skin condition that causes dry and itchy skin and also scaly patches, blisters, and skin infections. It is mostly common in childhood.
- Eczema is not contagious while scabies can be transmitted through personal contact.
- Eczema typically presents as red inflamed skin with dry patches while scabies presents with burrow tracks.
- Skin biopsy can help differentiate.
Distinguish Psoriaris from Scabies – Diagnosis
This is a complex chronic autoimmune condition that involves the buildup of the keratinocytes in the epidermis. Apart from immunological factors, environmental and genetic factors also play a role in development.
- Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder while scabies is an infestation by a mite.
- Psoriasis presents with thick red patches of skin covered with silvery scales while scabies presents with burrowed tracks.
- Psoriasis is non-contagious.
- Dermatological biopsy can be performed to differentiate.
Distinguish Folliculitis from Scabies – Diagnosis
This refers to the inflammation of the follicles, creating a follicular-based pustule, usually caused by either bacteria or fungi or a parasite or have a non-infectious etiology most commonly as a result of follicular trauma or occlusion.
- Folliculitis presents with red, pus-filled bumps around hair follicles while scabies presents with burrowed tracks.
- Thorough history and physical examination are performed to differentiate.
- Gram stain and bacterial culture can also be performed.
Distinguish Prurigo Nodularis from Scabies – Diagnosis
This is a chronic skin disorder which usually presents as multiple, intensely itching, excoriated nodules erupting on the extensor surfaces of the limbs secondary to itching or rubbing. The main cause is unknown.
- Prurigo nodularis normally develops after intense rubbing or scratching while scabies develops after infestation by mite.
- Scabies is contagious while prurigo nodularis isn’t.
- Scabies is mainly found in warm areas while prurigo nodularis is usually found in arms and legs.
- Skin biopsy can help differentiate.
Distinguish Dermatitis Herpetiformis from Scabies – Diagnosis
This is an autoimmune blistering disorder of the skin often associated with celiac disease. It is always bumpy and very itchy.
- DH is associated with celiac disease, which is a gluten-digesting problem while scabies is caused by a mite.
- DH presents with bumps and blisters while scabies presents with burrows as their hallmark.
- Biopsy and skin scraping examination can help differentiate.
Distinguish Erythema Multiforme from Scabies – Diagnosis
This is an acute and sometimes recurring skin condition theorized to be a type IV hypersensitivity reaction associated with certain triggers, e.g., infections, medications. The main symptom is a rash.
- Erythema multiforme is triggered by allergens while scabies is caused by mite infestation.
- Erythema multiforme’s lesions are typically symmetrical while scabies presents as small, blisters, and burrows in the skin.
Distinguish Pediculosis from Scabies – Diagnosis
This is a highly contagious disease caused by a parasite categorized into Pediculus humanus capitis, Pthirus pubis, Pediculus humanus humanus.
Distinguish Drug Eruptions from Scabies – Diagnosis
Refers to reactions on the skin due to prolonged medication intake. Some of the types of drug reactions include maculopapular eruption, urticaria, fixed drug eruption, erythema multiforme.
Important Red Flags with Scabies
Scabies significantly has the same symptoms with other conditions; therefore, thorough diagnostic procedures need to be done in order to differentiate it from others and administer appropriate treatment.
However, some of the red flags include:
- Worsening symptoms.
- Secondary infections.
- Spread to new areas.
- Persistent symptoms.
- Systemic symptoms.
- Reaction to medication.
