Contents
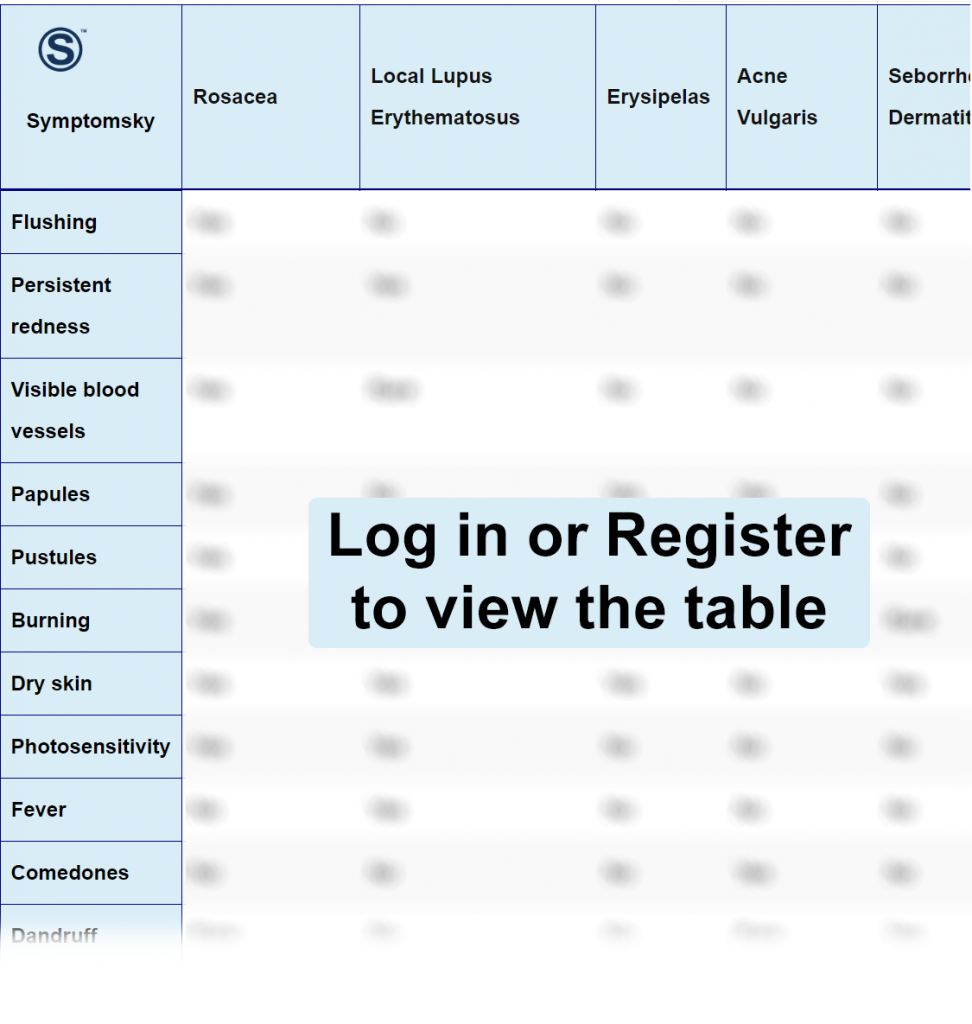
- 1 Rosacea Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How to Distinguish Rosacea from Other Diseases
- 2.1 Distinguish Local Lupus Erythematosus from Rosacea – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Erysipelas from Rosacea – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Acne Vulgaris from Rosacea – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish Seborrheic Dermatitis from Rosacea – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Eczema from Rosacea – Diagnosis
- 2.6 Distinguish Allergic Rash from Rosacea – Diagnosis
- 2.7 Distinguish Keratosis Pilaris from Rosacea – Diagnosis
- 2.8 Distinguish Demodicosis from Rosacea – Diagnosis
- 2.9 Distinguish Polymorphous Light Eruption from Rosacea – Diagnosis
- 3 Common Red Flags with Rosacea
Rosacea Differential Diagnosis Table:
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the center of the face (nose and cheeks). Rosacea is characterized by relapsing face flushing and telangiectasia (spider veins).
Diagnostic guidelines for Rosacea according to National Rosacea Society Experts are that Rosacea is clinically diagnosed if one of the following signs is present (redness in the center of the face or phymatous changes), or two of the following signs are present (papules, flushing, telangiectasia, or ocular manifestations).
How to Distinguish Rosacea from Other Diseases
Distinguish Local Lupus Erythematosus from Rosacea – Diagnosis
Local Lupus Erythematosus is a chronic autoimmune anti-inflammatory disease where any organ can be attacked by immune cells.
- Lupus erythematosus is characterized by a butterfly rash after sun exposure, but rosacea is characterized by spider veins.
- Local Lupus Erythematosus has systemic symptoms such as fatigue, joint pain, and fever. Local Lupus Erythematosus is found all over the body and is short-lived, but Rosacea only affects the face and is persistent.
“Blood and urine analysis are used for differentiation.”
Distinguish Erysipelas from Rosacea – Diagnosis
Erysipelas is a skin infection condition in the dermis layer.
- Erysipelas starts on the skin of the lower extremities, but Rosacea is only found on facial skin.
“Blood tests and C-reactive protein are used for differentiation.”
Distinguish Acne Vulgaris from Rosacea – Diagnosis
Acne vulgaris is an inflammatory disorder, including inflammatory and non-inflammatory lesions.
- Acne Vulgaris is found on the face, upper arms, back, and trunk, but Rosacea only affects the face.
“Acne Vulgaris and Rosacea are differentiated by comedones, which are absent in Rosacea and present in Acne Vulgaris.”
Distinguish Seborrheic Dermatitis from Rosacea – Diagnosis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic fungal disorder affecting skin areas concentrated with sebaceous glands.
- Seborrheic dermatitis causes yellow-greasy patches with scales, which do not happen in rosacea.
- Seborrheic dermatitis is found on the hairline and scalp, but Rosacea is found on facial skin.
“Dermascope is used for differentiation between Seborrheic dermatitis and Rosacea.”
Distinguish Eczema from Rosacea – Diagnosis
Eczema or atopic dermatitis is a common chronic inflammatory skin condition that happens as a result of skin barrier dysfunction.
- Eczema is associated with itching, but itching is absent in rosacea.
- Eczema affects children and is found on elbows, knees, and wrists, but rosacea is found on facial skin.
Distinguish Allergic Rash from Rosacea – Diagnosis
Allergic rash is an inflammation due to hypersensitivity.
- Allergic rash is found all over the skin of the body, but rosacea is found on facial skin.
“Patch test and skin biopsy are used for differentiation between Allergic rash and Rosacea.”
Distinguish Keratosis Pilaris from Rosacea – Diagnosis
Keratosis pilaris is an asymptomatic skin condition, where abnormal follicular keratinization occurs.
- Keratosis pilaris is found on upper and lower extremities, but rosacea is found on facial skin.
- Keratosis pilaris involves hair follicles, but hair follicles are not involved in Rosacea.
“Dermascope is used for differentiation between Keratosis pilaris and Rosacea.”
Distinguish Demodicosis from Rosacea – Diagnosis
Demodicosis is a colonization of Demodex mites.
- Demodicosis affects sebaceous glands and hair follicles, but in rosacea hair follicles and sebaceous glands are not affected.
“Skin surface biopsy (SSB) and Dermascope are used for differentiation between Rosacea and Demodicosis.”
Distinguish Polymorphous Light Eruption from Rosacea – Diagnosis
Polymorphous Light Eruption is an immunologically inflammatory disease due to sun exposure.
“Polymorphous light eruption appears as rashes on arms and lower legs. Polymorphous light eruption appears only after sun exposure, unlike Rosacea appears on the center of the face and is persistent.”
Common Red Flags with Rosacea
Rosacea has an environmental and genetic predisposition. Rosacea is incurable, but its symptoms can be limited and managed. Topical medications are used as long as symptoms are mild and fair, but in more aggressive progression oral medications are added. Patients should avoid triggers such as sun exposure, spicy food, stress, etc. Patients with rosacea should always be alert for ocular manifestations to avoid its progression. For mild ocular symptoms, eye hydration is considered.
