Contents
- 1 Pyogenic Granuloma Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How to Distinguish Pyogenic Granuloma from Other Diseases
- 2.1 Distinguish Amelanotic Melanoma from Pyogenic Granuloma – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Angiosarcoma from Pyogenic Granuloma – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) from Pyogenic Granuloma – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish Hemangiosarcoma from Pyogenic Granuloma – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Hemangioendothelioma from Pyogenic Granuloma – Diagnosis
- 2.6 Distinguish Bacillary Angiomatosis from Pyogenic Granuloma – Diagnosis
- 2.7 Distinguish Cutaneous Tuberculosis from Pyogenic Granuloma – Diagnosis
- 2.8 Distinguish Pseudocowpox from Pyogenic Granuloma – Diagnosis
- 3 Common Red Flags with Pyogenic Granulomas
Pyogenic Granuloma Differential Diagnosis Table:
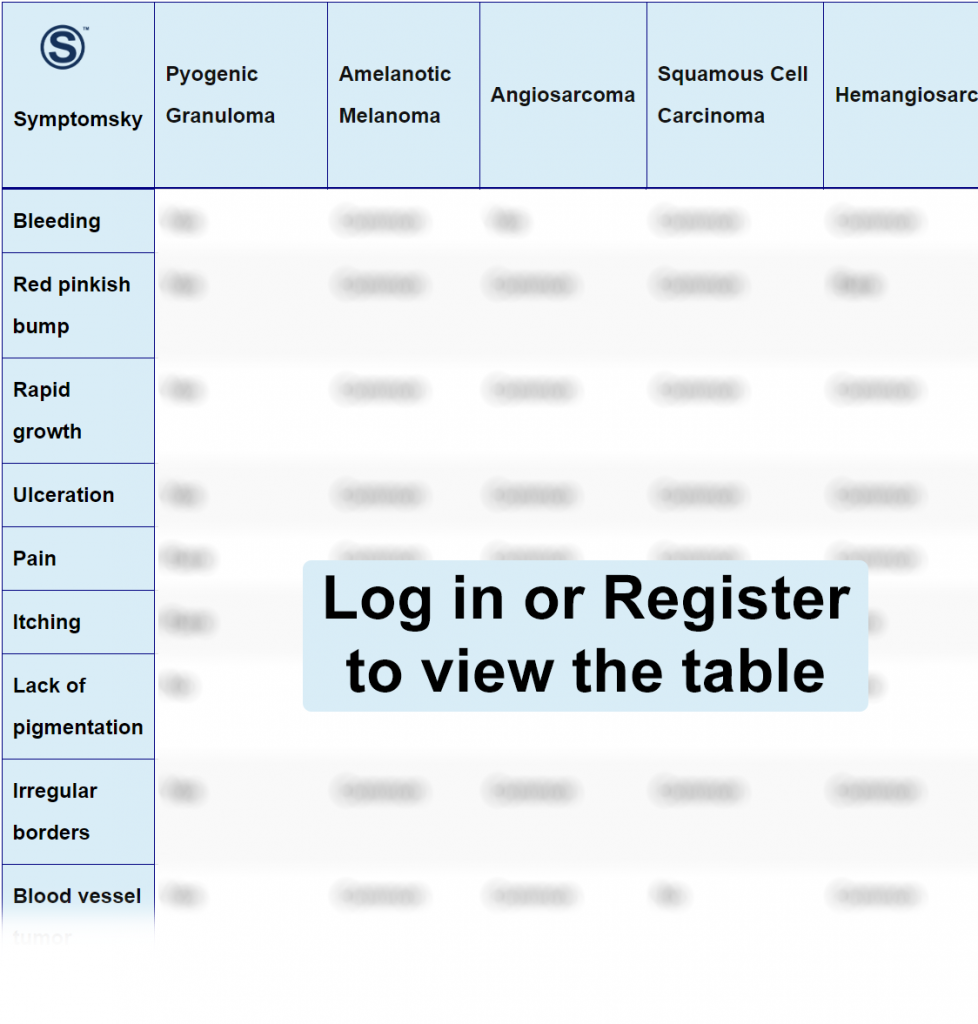
Pyogenic granuloma is a non-neoplastic proliferation of blood vessels with a tumor appearance. It is characterized by excessive proliferation of connective tissue in response to accidental trauma or aggression. It can develop on both skin and mucosa, with the oral mucosa being the most affected. It predominates at any age, and there is no distinction between gender. Risk factors include: Previous trauma, pregnancy, medications, and recent insect bites.
How to Distinguish Pyogenic Granuloma from Other Diseases
Distinguish Amelanotic Melanoma from Pyogenic Granuloma – Diagnosis
Amelanotic melanoma is a subtype of melanoma with a low diagnostic probability since the lack of melanin over the lesions makes the diagnosis more difficult. It is more frequently associated with white patients with phototype I disorder.
- Amelanotic melanoma main lesions are erythematous macules with epidermal changes due to the sun or ulcerated hemangioma-like nodules, while pyogenic granuloma lesions are pinkish rapidly growing vascularized nodules that may present superficial ulceration and bleed frequently.
- Pyogenic granuloma is a benign lesion, unlike amelanotic melanoma, which is a malignant lesion.
- Amelanotic melanomas are more common in patients over 50 years old, while most cases of pyogenic granuloma are described more frequently in young women, especially during pregnancy or in the use of contraceptives.
Distinguish Angiosarcoma from Pyogenic Granuloma – Diagnosis
Angiosarcomas are a high-malignancy proliferation of mixed cells.
- Clinical presentation consists of purple macules or red-violet nodules, and it has vascular and lymphatic components, while pyogenic granuloma lesions are pinkish rapidly growing vascularized nodules.
- Angiosarcomas have a mixed vascular and lymphatic cellular origin, while pyogenic granuloma only has an endothelial cellular origin.
Distinguish Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) from Pyogenic Granuloma – Diagnosis
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of cancer in the world. It appears on areas exposed to the sun such as the face, neck, nose, ears, and shoulders. Squamous cell carcinoma can develop or coexist on top of other present lesions.
- Squamous cell carcinoma lesions are scaly, thickened patches or plaques that form bloody scabs and may itch, while pyogenic granuloma lesions are pinkish rapidly growing vascularized nodules.
- Squamous cell carcinoma usually develops in areas of the body that are more exposed to the sun, while pyogenic granuloma lesions are frequent in the area of the head and neck.
Distinguish Hemangiosarcoma from Pyogenic Granuloma – Diagnosis
Hemangiosarcoma is a malignant endothelial tumor of blood vessels.
- Hemangiosarcoma can affect internal organs such as the liver and spleen, unlike pyogenic granuloma, which rarely affects the central nervous system and liver.
- Hemangiosarcoma has a predisposition in patients with light skin since this condition is induced by ultraviolet rays, while pyogenic granuloma is not linked to those characteristics.
- The lesions are rapidly growing red to blue color hematomas or raised papules, while pyogenic granuloma lesions are pinkish rapidly growing vascularized nodules.
Distinguish Hemangioendothelioma from Pyogenic Granuloma – Diagnosis
It is a rare and aggressive vascular tumor.
- Hemangioendothelioma mainly affects women, while pyogenic granuloma mainly affects children and young adults.
- Hemangioendothelioma can affect the liver, lungs, bones, and skin, unlike pyogenic granuloma, which rarely affects the central nervous system and liver.
- The lesions are flat red or brown spots in the organs that are affected, while pyogenic granuloma lesions are pinkish rapidly growing vascularized nodules.
Distinguish Bacillary Angiomatosis from Pyogenic Granuloma – Diagnosis
It occurs in HIV infections.
- Bacillary Angiomatosis lesions are bright red, violet, or skin-colored ulcerated papules or nodules in the dermis; they are firm and appear in any region while pyogenic granuloma lesions are pinkish rapidly growing vascularized nodules and usually present on arms and hands.
- Bacillary Angiomatosis lesions can be single or multiple, while pyogenic granuloma is usually a single lesion.
- Bacillary Angiomatosis occurs mostly in immunosuppressed patients while pyogenic granuloma does not present these epidemiological data.
- Bacillary Angiomatosis is an opportunistic infectious disease that produces cutaneous lesions while pyogenic granuloma is a benign vascular tumor lesion.
Distinguish Cutaneous Tuberculosis from Pyogenic Granuloma – Diagnosis
It is an infectious dermatosis due to the Koch bacillus.
- Cutaneous tuberculosis is transmitted through direct inoculation while pyogenic granuloma does not have a transmission pathway.
- Cutaneous tuberculosis is a chronic infection while pyogenic granuloma is not a contagious condition.
- Cutaneous tuberculosis lesions are erythematous ulcerative nodules with well-defined edges and rapid progression that can also present fistulas, while pyogenic granuloma lesions are pinkish rapidly growing vascularized nodules.
Distinguish Pseudocowpox from Pyogenic Granuloma – Diagnosis
This viral condition occurs in farmworkers when they come into direct contact with contaminated fomites.
- Pseudocowpox lesions are flattened erythematous papules that later progress into firm violet nodules forming crusts with central depression while pyogenic granuloma lesions are pinkish rapidly growing vascularized nodules.
- Pseudocowpox nodules can be solitary or multiples, unlike pyogenic granuloma; they are usually solitary.
- Pseudocowpox is a viral condition while pyogenic granuloma is not.
Common Red Flags with Pyogenic Granulomas
Pyogenic Granulomas can also appear within the gastrointestinal tract. They appear from the second to the third trimester of pregnancy within the oral mucosa, over the gingiva due to hormonal pregnancy changes. It is necessary to educate the patient to avoid picking the lesion to prevent additional traumas or infections. It can resurface if it is not completely removed.
Although the origin of this condition is not linked to the presence of bacteria, it is important to educate our patient about good oral hygiene since dental tartar favors the appearance of this condition.
