Contents
- 1 Phlebitis Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How To Distinguish Phlebitis From Other Diseases
- 2.1 Distinguish Phlebitis from Cellulitis – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Phlebitis from Deep Vein Thrombosis – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Phlebitis from Venous Insufficiency – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish Phlebitis from Superficial Thrombophlebitis – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Phlebitis from Lymphangitis – Diagnosis
- 3 Common Red Flags with Phlebitis
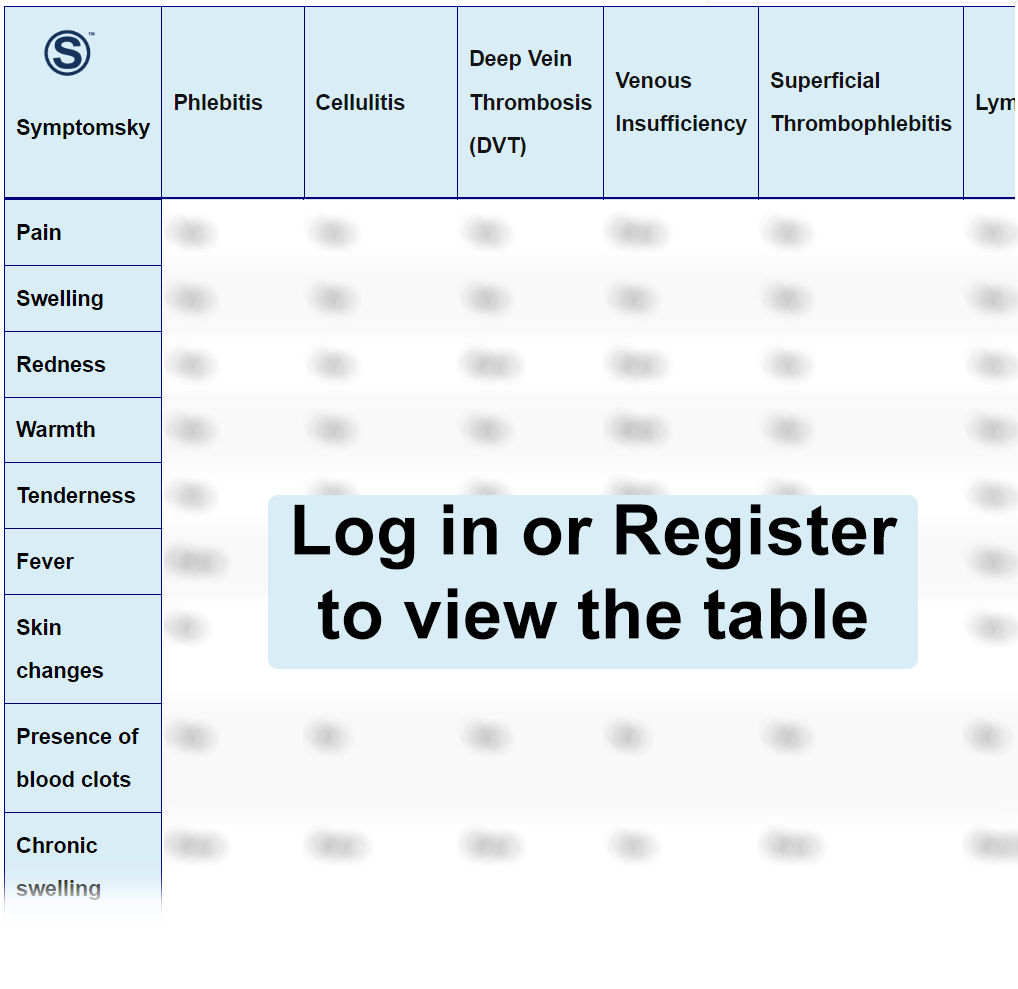
Phlebitis Differential Diagnosis Table:
The venous circulatory system is essential for health, the main reason being that it is responsible for maintaining the balance of the organism in various ways by purifying the blood of toxic substances and ensuring that it receives necessary nutrients by returning it to the heart and pumping it systemically, as well as favoring the proper distribution of blood flow, regulating the temperature of the skin, and maintaining the body’s water and electrolyte balance. Circulatory disorders are very common nowadays, so their clinical management is very important for the patient’s survival and quality of life. Phlebitis is the most common peripheral circulatory disorder of the skin.
Phlebitis is the inflammation of the blood vessel walls accompanied by alteration of the vascular endothelium. According to its characteristics, phlebitis can be classified into superficial and deep phlebitis. Superficial phlebitis, as its name indicates, affects the superficial part of the skin, and deep phlebitis is the result of a blood clot.
The most frequent and well-known causes of phlebitis are infectious diseases, trauma, deep vein thrombosis, surgery, certain immune diseases such as lupus or polymyalgia rheumatica, and lifestyle factors such as sedentarism, smoking, and obesity. People with cancer, autoimmune diseases, pregnant women, women under contraceptive treatment, and chronic alcoholics are more susceptible to this condition. Pain and discomfort are the first signs of phlebitis and may be accompanied by swelling and warmth, as well as discoloration around the affected area, fever in some cases, and the sign of a palpable cord symptom in which the swelling and pain on palpation can be felt.
How To Distinguish Phlebitis From Other Diseases
Distinguish Phlebitis from Cellulitis – Diagnosis
It is a skin infection.
- Cellulitis, unlike Phlebitis, is a bacterial skin infection.
- Cellulitis is characterized by a lesion without limited edges, edematous, tender to the touch, painful, warm; it may be present with red spots, blisters, and has the appearance of orange peel, while pain and discomfort are the first signs of Phlebitis, which may be accompanied by swelling and warmth as well as discoloration around the affected area, fever in some cases, and the sign of a palpable cord symptom in which the swelling and pain on palpation can be felt.
- Patients with Cellulitis have fever and general malaise and may even show signs of sepsis such as hypotension and tachycardia, unlike Phlebitis in which these symptoms are rare.
- Cellulitis diagnosis is made by exudate culture, while Phlebitis diagnosis is based on duplex ultrasound findings.
Distinguish Phlebitis from Deep Vein Thrombosis – Diagnosis
It is partial or total obstruction of the deep venous system of an extremity.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis symptoms, unlike Phlebitis, are oppressive pain and unilateral edema with increased temperature of the affected area.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis contributing factors, unlike Phlebitis, are venous stasis, vascular injury, and hypercoagulability.
Distinguish Phlebitis from Venous Insufficiency – Diagnosis
It is the inability of venous return.
- Venous insufficiency, as opposed to Phlebitis, produces heaviness, swelling in the lower legs and ankles, night cramps, dryness, and constant itching, as well as dermal signs such as hyperpigmentation or dermatitis.
Distinguish Phlebitis from Superficial Thrombophlebitis – Diagnosis
- Unlike Phlebitis, Superficial Thrombophlebitis is an inflammatory process in which a blood clot is formed, blocking superficial veins.
Distinguish Phlebitis from Lymphangitis – Diagnosis
- Lymphangitis is the inflammation of superficial lymphatic vessels caused by infection, while Phlebitis is the inflammation of the blood vessel walls accompanied by alteration of the vascular endothelium.
- Lymphangitis, unlike Phlebitis, presents fever and absence of blood clots.
Common Red Flags with Phlebitis
For the diagnosis of Phlebitis, the clinical history and a good physical examination are essential because symptoms and associated risk factors will be present, but the most commonly used complementary test is the duplex ultrasound because it is sensitive and specific to detect it.
As for the treatment, it will depend on the comorbidities, location, symptoms, and extent of the lesion. For superficial phlebitis, it will be treated symptomatically by hot compresses, raising the affected limb, walking, and with the use of NSAIDs. If the cause of venous origin is identified, it must be changed. For deep phlebitis, an anticoagulation therapy for 45 days is required, and surgical measures include the removal and ligation of veins as a curative measure.
Phlebitis and other vascular conditions can be prevented by taking care of blood circulation by avoiding sitting for a long time, using compression socks, walking and stretching your legs, drinking a lot of fluids, as well as stopping smoking.
Among the complications of Phlebitis are local infections, abscess, the progress of a superficial phlebitis to a deep phlebitis, and pulmonary thromboembolism.
