Contents
- 1 Pernicious Anemia Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How to Distinguish Pernicious Anemia from Other Diseases
- 2.1 Distinguish Iron Deficiency Anemia from Pernicious Anemia – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Chronic Kidney Disease from Pernicious Anemia – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Chronic Liver Disease from Pernicious Anemia -Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish Hypothyroidism from Pernicious Anemia – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Folate Deficiency Anemia from Pernicious Anemia – Diagnosis
- 2.6 Distinguish Hemolytic Anemia from Pernicious Anemia -Diagnosis
- 3 Common Red Flags with Pernicious Anemia
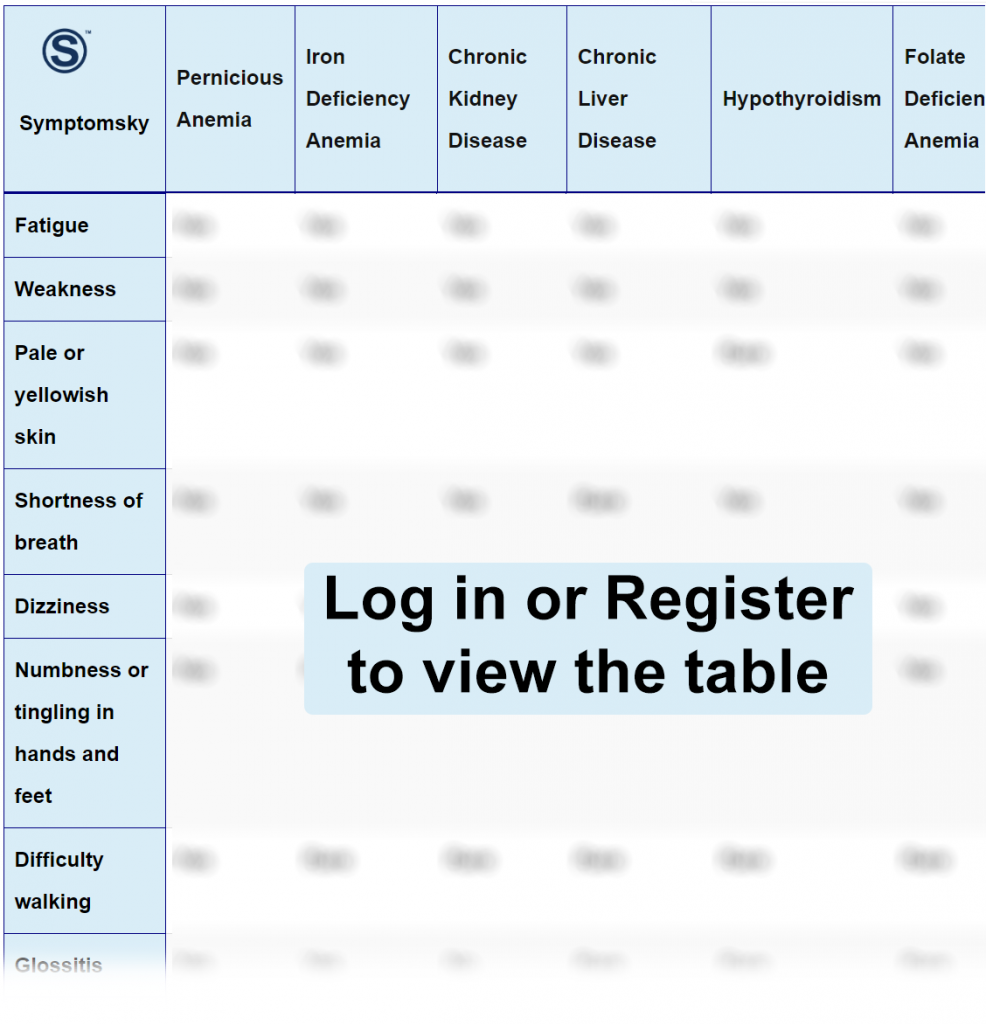
Pernicious Anemia Differential Diagnosis Table:
Anemia is defined as the decrease in the number of red blood cells. Red blood cells are responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the whole organism as well as giving color to the blood. In order to perform this transportation, a protein called hemoglobin is needed. Red blood cells are manufactured in the bone marrow, which is found inside the bones. For the proper manufacture of red blood cells, an amount of iron, folic acid, and vitamins essentially, Vitamin B12 or Cobalamin is also needed. The deficiency of Vitamin B12 or Cobalamin is called Pernicious Anemia.
Pernicious Anemia is a blood disease caused by the lack of a substance called intrinsic factor that the body needs to absorb Vitamin B12. In Pernicious Anemia, the body produces antibodies that destroy the parietal cells which are the cells in the stomach responsible for producing intrinsic factor, the body also produces antibodies that block the action of intrinsic factor.
90% of the causes of Pernicious Anemia are due to an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the intrinsic factor protein so the Vitamin B12 will not be absorbed, the other 10% is due to atrophic gastritis, or the low consumption of food containing this vitamin which are: beef, seafood, eggs, and dairy products. Pernicious Anemia may even be congenital.
People who have a higher risk of presenting this disease are: people over 60 years of age, however, it can be present during childhood known as Youth Pernicious Anemia, European Nordic people, people with a family history of this condition, people who have undergone gastric surgeries, also are related to other autoimmune conditions such as: Hashimoto´s disease, Grave´s disease, Type 1 Diabetes, Crohn Disease, Celiac Disease, and Systemic lupus erythematosus.
The clinical picture consists of: palpitations, sweating, cardiac failure, asthenia, anorexia, diarrhea, angular stomatitis, glossitis, can also present neurological alterations such as follicular myelosis, ataxia, attenuated to falls, as well as irritability and dementia.
In my experience, I have had two different patients with this condition, the first a young patient in his 30s who had been on a vegan diet for 3 years presenting tiredness and fatigue at the moment of exercising as well as another extreme, totally different scenario, an older patient in his 60s with a history of gastric carcinoma and therefore a total gastrectomy presenting, pale skin, Hunter’s glossitis, and ataxia.
How to Distinguish Pernicious Anemia from Other Diseases
Distinguish Iron Deficiency Anemia from Pernicious Anemia – Diagnosis
Iron Deficiency Anemia is characterized by the decrease in the absence of iron deposits in the blood.
- Iron Deficiency Anemia, unlike Pernicious Anemia, is the most frequent type of anemia.
- Iron Deficiency Anemia, unlike Pernicious Anemia, is the most frequent type of anemia and is more prevalent in pregnancy and lactation.
- Iron Deficiency Anemia symptoms are: irritability, lability, headache, fatigue, paresthesias, eating disorders such as PICA (excessive appetite for unusual substances), fragility of the nails and hair, Plummer-Vinso syndrome, koilonychia, while Pernicious Anemia symptoms are palpitations, sweating, cardiac failure, asthenia, anorexia, diarrhea, angular stomatitis, glossitis, can also present neurological alterations such as follicular myelosis, ataxia, attenuated to falls, as well as irritability and dementia.
- Iron Deficiency Anemia diagnosis is made by the following laboratory tests: complete blood count, serum iron levels, serum ferritin levels, transferrin saturation, iron binding capacity, and hemoglobin levels while Pernicious Anemia laboratory tests are serum Vitamin B12 levels, anti-intrinsic factor antibodies, serum gastrin level, and Schilling Test.
Distinguish Chronic Kidney Disease from Pernicious Anemia – Diagnosis
It is the loss of the functionality of the kidneys.
- Pernicious Anemia is due to an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the intrinsic factor protein so the Vitamin B12 will not be absorbed while Chronic Kidney Disease Anemia is due to insufficient production of erythropoietin.
- Kidney Disease Anemia treatment, unlike Pernicious Anemia, can be based on changes in diet or subcutaneous injection of erythropoietin during dialysis.
Distinguish Chronic Liver Disease from Pernicious Anemia -Diagnosis
It consists of the terminal stage of chronic liver disease.
- Pernicious Anemia is due to an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the intrinsic factor protein so the Vitamin B12 will not be absorbed while Chronic Liver Disease Anemia is due to liver damage, producing malabsorption of the nutrients especially folic acid and vitamin B12.
- Chronic Liver Disease Anemia patients, unlike Pernicious Anemia patients, may present gastrointestinal bleeding, coagulopathy, jaundice, and splenomegaly due to portal hypertension.
Distinguish Hypothyroidism from Pernicious Anemia – Diagnosis
It is the hypoactivity of the thyroid gland.
- Pernicious Anemia is due to an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the intrinsic factor protein so the Vitamin B12 will not be absorbed while Anemia is a secondary cause of Hypothyroidism.
- Hypothyroidism, unlike Pernicious Anemia, does not present neurological symptoms unless it evolves to a myxedematous coma.
Distinguish Folate Deficiency Anemia from Pernicious Anemia – Diagnosis
It is the deficiency of folic acid in the blood.
- Pernicious Anemia is due to an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the intrinsic factor protein so the Vitamin B12 will not be absorbed while Folate Deficiency Anemia’s cause is multifactorial since it may be due to an unbalanced diet, alcoholism, diseases of the digestive tract, pregnancy, genetic factors, and certain medications that are used to prevent seizures.
- Folate Deficiency Anemia, unlike Pernicious Anemia, does not cause neurological alterations but presents diarrhea.
- Folate Deficiency Anemia diagnosis is made by measuring the serum levels of folic acid, complete blood count, and homocysteine concentration levels while Pernicious Anemia laboratory tests are serum Vitamin B12 levels, anti-intrinsic factor antibodies, serum gastrin level, and Schilling Test.
Distinguish Hemolytic Anemia from Pernicious Anemia -Diagnosis
It is an insufficient amount of healthy red blood cells since they are destroyed earlier than normal.
- Pernicious Anemia is due to an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the intrinsic factor protein so the Vitamin B12 will not be absorbed while Hemolytic Anemia cause is multifactorial since it may be due to sickle cell anemia, infections, anti-malaria medication, leukemia, autoimmune diseases, tumors, hypersplenism or autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
- Hemolytic Anemia, unlike Pernicious Anemia, presents hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, and coluria.
- Hemolytic Anemia diagnosis is made by a complete blood count, urine tests, biopsy of the bone marrow while Pernicious Anemia laboratory tests are serum Vitamin B12 levels, anti-intrinsic factor antibodies, serum gastrin level, and Schilling Test.
Common Red Flags with Pernicious Anemia
The diagnosis of Pernicious Anemia is based on clinical presentation, laboratory tests measuring serum Vitamin B12 levels, anti-intrinsic factor antibodies, serum gastrin level, Schilling Test, and gastroscopic imaging studies.
Treatment consists of Vitamin B12 supplementation through intramuscular injections or oral tablets as well as nasal spray, since this is a condition in which the body may not be able to absorb this vitamin through food, supplementation should be continued for life.
Pernicious Anemia has a good prognosis, especially if treatment is started early; late diagnosis and treatment can cause irreversible neurological damage.
Complications of Pernicious Anemia include: neurological damage such as tingling or numbness of the hands and feet, cardiac problems such as palpitations, heart failure, can cause pregnancy complications, increased risk of infections as well as an increased risk of gastric cancers.
There is no way to prevent Pernicious Anemia but its complications can be avoided if detected early.
