Contents
- 1 Molluscum Contagiosum Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How To Distinguish Molluscum Contagiosum from Other Diseases
- 2.1 Distinguish Seborrheic Keratosis from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Viral Warts from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Condylomata Acuminata from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish Eczema from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Acne from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
- 2.6 Distinguish Folliculitis from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
- 2.7 Distinguish Skin Tags from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
- 2.8 Distinguish Herpes Simplex Virus from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
- 2.9 Distinguish Varicella from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
- 2.10 Distinguish Basal Cell Carcinoma from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
- 3 Important Red Flags in Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum Contagiosum Differential Diagnosis Table:
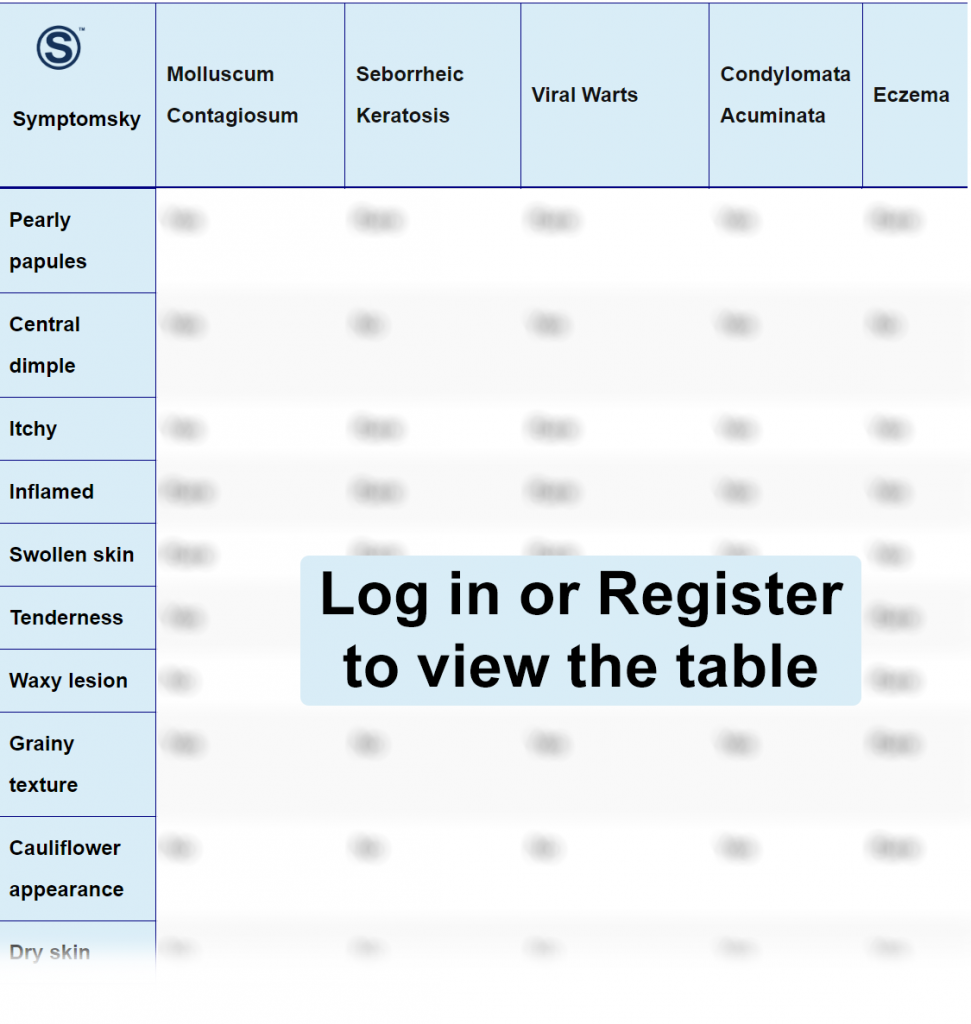
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral infection caused by poxvirus. It causes skin nodules that are white-pink in color and look like pearls; they are usually small in size, about 2-5 mm in diameter.
Molluscum contagiosum is a contagious infection, but it usually resolves on its own without any complications. Complete resolution may take up to a few years.
The diagnosis of this infection usually depends on its appearance, but in some cases, if a lot of differentials are present, a sample of the nodules may be taken to be examined under a microscope.
How To Distinguish Molluscum Contagiosum from Other Diseases
Distinguish Seborrheic Keratosis from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
Seborrheic keratosis is a very common skin growth. It’s a benign skin tumor that affects almost everyone, especially geriatrics, and its incidence increases with age. In most cases, seborrheic keratosis is asymptomatic, but in some rare cases, it can develop some itching or bleeding. You can ask your doctor to remove it if it bothers you.
- Usually, your doctor can examine and diagnose seborrheic keratosis by the naked eye.
- In some cases, your doctor may use a dermascope to confirm the diagnosis of seborrheic keratosis.
“Some suggest that a biopsy may be needed to confirm the benign growth of the tumor, but in practice, that is rarely needed.”
Distinguish Viral Warts from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
Viral warts are a common viral infection caused by human papillomavirus. It’s very contagious and transmits easily by direct contact and touch. It leads to small bumps on the skin and forms in clusters. They most commonly appear on hands and feet. They are usually very harmless and go away on their own, but it can take up to a few months to resolve.
- Viral warts can easily be diagnosed just by visual examination by a doctor. Sometimes a doctor may use a dermoscope to help in visualization.
- A biopsy is rarely needed, but your doctor may need it to make a confirmative diagnosis and rule out any cancerous growth.
Distinguish Condylomata Acuminata from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
Condylomata acuminata, also known as anogenital warts, are caused by HPV infection, but they occur only on the genital area and are transmitted by unprotected sexual intercourse. They can occur in mucosa too by oral sex, and they have a unique cauliflower-like appearance. Sometimes they can be itchy.
- Diagnosis of condylomata acuminata can be by simple visual examination because of its characteristic cauliflower-like appearance.
- A biopsy may be needed if the bumps are atypical from anogenital warts, especially in old and immunocompromised patients.
- A pap smear in females is sometimes needed to detect any abnormal vaginal changes.
Distinguish Eczema from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
Eczema is a very common chronic condition that causes dry, itchy skin. It usually happens because of allergies, and people with eczema usually have other food allergies and hay fever. There’s no cure for eczema, and it’s not contagious either, but treatment with moisturizers can help ease the itching during flare-ups of the disease.
- Diagnosis of eczema mainly depends on the physical appearance and history of the patient.
- A patch test may be needed to help determine if there’s a special kind of allergen causing eczema.
- Rarely, a skin biopsy is needed, but sometimes your doctor will need to confirm which type of eczema you have.
Distinguish Acne from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
Acne is a skin condition that affects people from age 12 to almost 30, and in some cases, it can continue with older people. Acne happens because of a lot of reasons, but it’s mainly because the hair follicle becomes clogged, and sebum that supposedly pours out of the skin through small pores becomes clogged too, leading to white and blackheads. Acne can vary in size and severity from very small pimples to large pustules and can occur anywhere on the body, but it most commonly occurs on the face.
- Diagnosis of acne is very easy for the doctor by clinical examination, usually, there are no tests required for the diagnosis of acne.
- Blood tests or hormone levels may be needed if acne is severe or sudden and recurrent to see if there’s an underlying condition that causes acne.
Distinguish Folliculitis from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
Folliculitis is an inflammation of hair follicles on the skin, resulting in acne-like pimples. This can happen because of environmental factors like sweating or due to an infection, either bacterial or fungal.
- Diagnosis of folliculitis mainly depends on clinical examination where doctors see if the hair follicle is inflamed.
- A swab from the skin to be taken for bacterial culture is required to detect any bacterial infection.
- Scrapping of the skin to see if there’s a yeast growth under the skin.
- In some rare cases, a skin biopsy may be needed for confirmation and exclusion of any other conditions.
Distinguish Skin Tags from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
Skin tags, also known as acrochordon, are harmless skin growths that happen in areas where much rubbing occurs, like the neck, armpit, or groin. They usually happen in old-aged people. Skin tags don’t require any treatment, but if they bother you, you can ask your doctor to remove them.
- Skin tags don’t require any specific tests, but you should always see your doctor if you see any skin abnormality.
- A skin biopsy may be needed in some rare cases if a risk for malignancy is present.
Distinguish Herpes Simplex Virus from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
Herpes simplex virus is a very common viral infection that affects more than 60% of people. It’s highly contagious through direct contact, forming small red pimples that may be itchy or painful. It occurs either around the mouth and lips or around genital areas since there are two types of HSV: HSV1 and HSV2.
- A swab from the lesion can be taken to culture to confirm herpes simplex virus infection.
- A blood test for the detection of HSV antibodies can be used too.
- A piece from the lesion can be taken to be used for testing using PCR, which is more diagnostic for HSV than viral culture.
“In some cases, the doctor may ask you to do an MRI to see if the viral infection has reached the brain if you have shown any neurological symptoms.”
Distinguish Varicella from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
Varicella, also known as chickenpox, is a viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It’s highly contagious, and most unvaccinated people get it. It causes small, itchy, fluid-filled blisters all over the body and takes a few days to go away on their own.
- The Tzanck test is a very simple office-based test, and a positive Tzanck test is usually diagnostic for chickenpox.
- A blood test for the detection of varicella antibodies can help in diagnosis.
- The most diagnostic test is taking a part of the blister to be tested using PCR for the detection of the virus.
Distinguish Basal Cell Carcinoma from Molluscum Contagiosum – Diagnosis
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer. It usually occurs due to long exposure to UV lights from the sun and tends to occur more in people with light skin. Once this type of cancer is diagnosed early, it can be curable with treatment.
- A skin biopsy is the most diagnostic test for basal cell carcinoma.
- A PET scan may be needed to make sure that the cancer hasn’t spread to any internal organs or lymph nodes.
Important Red Flags in Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is usually a self-limited disease that can resolve on its own. They are often small in size but can appear very large too. It’s important to know that during healing, the area may be inflamed and swollen. It’s important not to touch this area since there’s an increased risk of secondary bacterial infection.
Scarring may occur during healing too if the area is scratched a lot, so it’s important to follow a special care plan for this part.
