Contents
- 1 Malignant Neoplasm Of The Colon Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How To Distinguish Malignant Neoplasm Of The Colon From Other Conditions
- 2.1 How to Distinguish Malignant Neoplasm of The Colon from Irritable Bowel Syndrome – Diagnosis
- 2.2 How to Distinguish Malignant Neoplasm of Colon from Colorectal Polyps -Diagnosis
- 2.3 How to Distinguish Malignant Neoplasm of Colon from Gastroenteritis – Diagnosis
- 2.4 How to Distinguish Malignant Neoplasm of Colon from Inflammatory Bowel Disease – Diagnosis
- 2.5 How to Distinguish Malignant Neoplasm of Colon from Diverticulitis – Diagnosis
- 3 Common Red Flags With Malignant Neoplasm Of The Colon
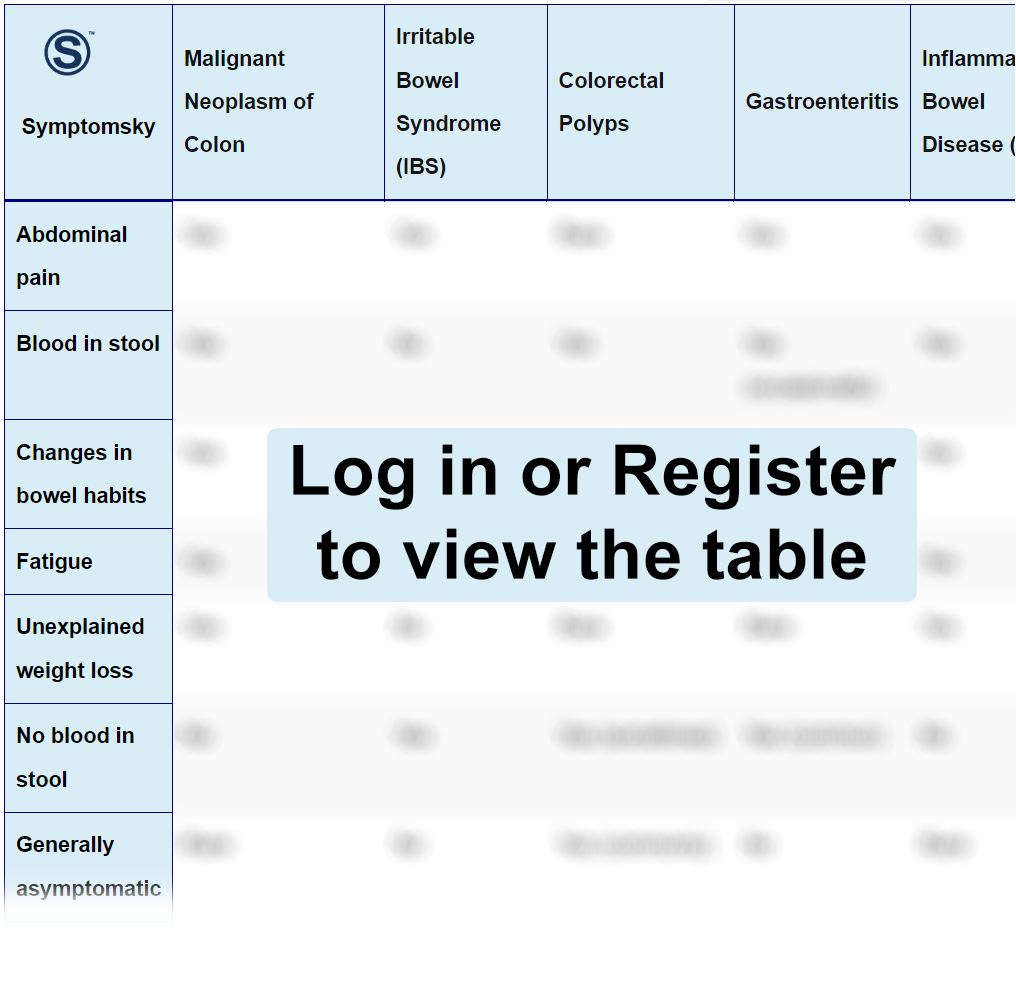
Malignant Neoplasm Of The Colon Differential Diagnosis Table:
Also known as colon cancer, this is the growth of abnormal cells in the colon. It is a multifactorial disease process with causes including genetic factors, environmental exposures, and inflammatory conditions of the digestive tract. Older people are at a higher risk of developing colon cancer.
Common symptoms include diarrhea, constipation, blood in stool, abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and low iron levels. However, the condition rarely has symptoms in the early stages. Diagnosis includes laboratory tests, which include complete blood count, chemistries and liver function tests, and serum carcinoembryonic antigen.
Imaging studies may include abdominal barium study, abdominal/pelvic CT, colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, and positron emission tomography. Surgery is the only curative modality for localized colon cancer, which provides the only curative option for patients with limited metastatic disease in the liver or lung. Other treatments may include immunotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and chemotherapy.
How To Distinguish Malignant Neoplasm Of The Colon From Other Conditions
How to Distinguish Malignant Neoplasm of The Colon from Irritable Bowel Syndrome – Diagnosis
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder of the digestive system encompassing the movement of the intestines, sensitivity of the nerves of the intestines, and the way the brain controls these functions, causing recurring abdominal pain and constipation or diarrhea.
- IBS is most common in young adults, while colon cancer mostly occurs in people of older age.
- Colon cancer usually presents with blood in stool, while IBS does not.
How to Distinguish Malignant Neoplasm of Colon from Colorectal Polyps -Diagnosis
Colorectal polyps are a benign growth on the lining of the colon or rectum.
- Most polyps are usually noncancerous, while colon cancer is usually malignant.
- Diagnosis is done through colonoscopy.
Polyps usually have the potential of becoming cancerous over time, resulting in colon cancer.
How to Distinguish Malignant Neoplasm of Colon from Gastroenteritis – Diagnosis
This is a contagious infection of the gut causing inflammation of the lining of the digestive system. It is caused by bacteria, parasites, viruses, and toxins.
- Diagnosis of gastroenteritis usually involves stool cultures for bacteria or viruses, while diagnosis of colon cancer includes different imaging.
How to Distinguish Malignant Neoplasm of Colon from Inflammatory Bowel Disease – Diagnosis
IBD describes two sets of diseases of the intestinal tract, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- IBD is an autoimmune disorder, while colon cancer is an abnormal growth of cells caused by different factors, including environmental factors.
- Diagnosis of IBD includes biopsies, endoscopy, and colonoscopy.
How to Distinguish Malignant Neoplasm of Colon from Diverticulitis – Diagnosis
Diverticulitis is the inflammation of one or more balloon-like sacs in the large intestines.
- Fever is common in diverticulitis due to infection, while it is less common in colon cancer.
- Diverticulitis is primarily diagnosed with a CT scan showing inflamed diverticula, while colon cancer is diagnosed using colonoscopy.
Common Red Flags With Malignant Neoplasm Of The Colon
More gradual onset, with pain that can be more diffuse and accompanied by systemic symptoms like weight loss and fatigue.
More likely to have visible blood in stool or occult blood, leading to anemia.
Diagnosed with colonoscopy and biopsy confirming malignancy.
