Contents
- 1 Lichen Planus Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 Distinguish Lichen Planus from Other Diseases
- 2.1 How to Distinguish Syphilis from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
- 2.2 How to Distinguish Exanthematous Drug Eruption from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
- 2.3 How to Distinguish Eczema from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
- 2.4 How to Distinguish Psoriasis from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
- 2.5 How to Distinguish Contact Dermatitis from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
- 2.6 How to Distinguish Pityriasis Rosea from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
- 2.7 How to Distinguish Lupus Erythematosus from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
- 2.8 How to Distinguish Tinea Corporis from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
- 2.9 How to Distinguish Fungal Infections from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
- 3 Important Red Flags in Lichen Planus
Lichen Planus Differential Diagnosis Table:
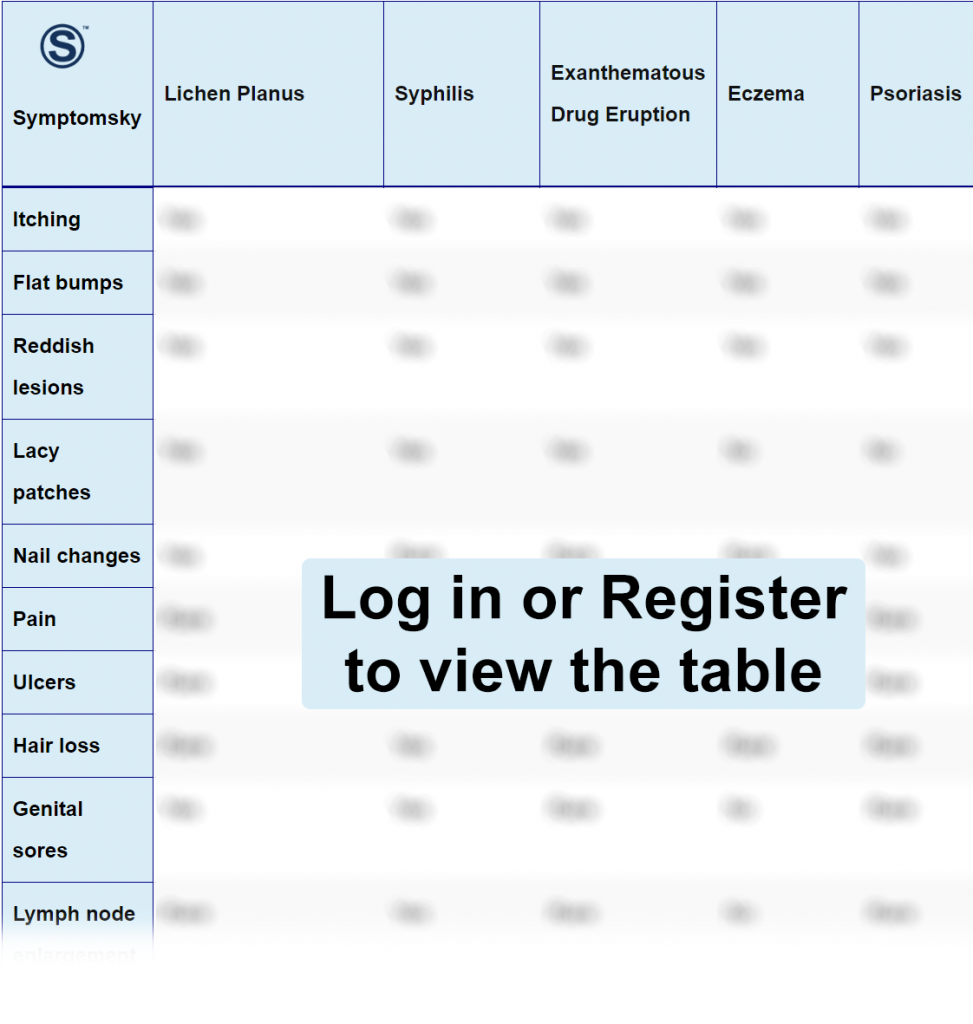
Lichen planus is a skin inflammatory condition that causes a rash in different body areas: arms, neck, legs, scalp, nails, mouth, and genitals.
They appear as raised red lesions that form as clusters on the skin that can be itchy, but in the mouth and genital areas, they may cause sores.
The exact cause of lichen planus is not known; it’s not an autoimmune disease, but it may be immune-mediated, as a reaction from a drug, a disease, or dental filling.
Lichen planus doesn’t have a treatment; they usually clear up on their own in 6 to 9 months (in some cases maybe more), but some medication can help relieve symptoms.
Distinguish Lichen Planus from Other Diseases
How to Distinguish Syphilis from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by a bacterial infection. During the secondary stage of syphilis, a rash starts to appear in different areas of the body. It may not be itchy and is variable in appearance; sometimes it’s so faded that it may be unnoticeable.
The most problematic aspect of syphilis rash is that it can be mistaken for other conditions easily.
- Serological blood tests to detect antibodies against syphilis are the most diagnostic tests.
- A lumbar puncture and CSF analysis that show high WBC, neutrophils, and positive VDRL can be used in diagnosis.
- Fluid from the sores itself can be taken and examined under a microscope to confirm syphilis.
How to Distinguish Exanthematous Drug Eruption from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
Exanthematous drug eruption, also known as morbilliform drug reaction, is a common cutaneous adverse reaction to drugs, most commonly antibiotics. Other categories can cause this reaction as well. It appears as a maculopapular red rash on the body, causing itching, and sometimes, low-grade fever can occur. It usually happens two weeks after exposing to the drug.
- Diagnosis of exanthematous drug eruption depends mainly on physical examination and detailed patient history.
- Skin biopsy is rarely needed and not routinely recommended, but in case of severe reaction, it may be required.
“Due to the lack of specific diagnostic tests for drug eruption, this condition is easily misdiagnosed, and diagnosis can be delayed.”
How to Distinguish Eczema from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
Eczema, known as dermatitis, is a common chronic skin condition that causes dry patches on the skin, causing itching. Eczema is an allergic reaction that occurs when the body comes in contact with an allergen. People with eczema can also have hay fever or asthma.
- Diagnosis of eczema mainly depends on physical examination and history of the patient.
- A patch test can help diagnose dermatitis, where the patient’s skin comes in contact with several substances to trigger a reaction.
- Sometimes a biopsy is needed not only to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions but also to help differentiate dermatitis types from each other.
How to Distinguish Psoriasis from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune chronic disease that causes skin to shed very quickly, leading to scaly silver patches on the skin, which is very characteristic of psoriasis. It’s a chronic condition, and the symptoms can be relieved by treatment, but flare-ups occur from time to time.
- Diagnosis of psoriasis depends mainly on physical examination and the presence of the characteristic silver scaly patches.
- A skin biopsy can be taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
How to Distinguish Contact Dermatitis from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
Contact dermatitis is a type of eczema that is triggered once the skin comes in contact with a known allergen. This leads to activation of the immune system, causing skin inflammation and rash. This usually resolves upon its own after removing the causative agent.
- Patch testing is often used to help in the diagnosis of contact dermatitis. The patch will stay on the skin for 2 to 3 days to see if any reaction will occur.
- A skin prick test can also be used, although it might not be completely useful in contact dermatitis. But it can help confirm the diagnosis with the patient’s clinical presentation and history.
“Contact dermatitis is usually easily diagnosed by physical appearance. The challenging part is usually trying to find the causative allergen to prevent recurrence of symptoms again.”
How to Distinguish Pityriasis Rosea from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
Pityriasis rosea is a skin rash that causes oval-shaped patches on the skin. This patch is known as herald patches and they are very characteristic of the disease. The exact cause of pityriasis rosea is unknown, maybe from a viral infection. This rash usually takes several weeks and resolves completely.
- Pityriasis rosea diagnosis is mainly made on physical examination (appearance of herald patches).
- A skin biopsy or skin scraping is sometimes needed to confirm the diagnosis if the physical appearance is not definitive.
“Serological tests for HHV6 are not routinely recommended since most people had antibodies against the virus since childhood.”
How to Distinguish Lupus Erythematosus from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
Lupus erythematosus is a skin condition caused by systemic lupus erythematosus (an autoimmune disease that makes the body attack healthy tissues and organs). When this condition affects the skin, it causes a butterfly rash, which appears mainly on the nose and face. The symptoms can be very severe, including most of the body parts and look like a red ring shape.
- Measuring ANA is very common to establish a diagnosis of lupus, since it’s almost positive in all lupus patients, but it has low specificity since it’s positive in other conditions too.
- A skin biopsy can help in confirming lupus affecting the skin specifically.
“Other tests like CBC, ERS, and CRP can help in monitoring disease prognosis.”
How to Distinguish Tinea Corporis from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
Tinea corporis is a fungal infection commonly known as ringworm. It causes a characteristic lesion of the skin (face, trunk, scalp) which is itchy and red. This is very common in humid, hot areas. This disease is very contagious but it is easy to treat with OTC medication.
- Skin scraping and examining it under a microscope with 20% KOH can confirm the diagnosis by looking for hyphae and spores.
- Fungal culture to confirm tinea infection, especially if microscopic examination is negative.
“Tinea corporis can easily be diagnosed just by clinical appearance (the characteristic ringworm) but confirmative diagnostic test is presence.”
How to Distinguish Fungal Infections from Lichen Planus – Diagnosis
Fungal infections can affect the skin, causing rash and red bumps on the skin. They can affect the face, but they are most commonly found in the nails and foot. Fungal infections are easily treated with topical cream, and in some rare cases, they may require systemic treatment. The duration of treatment for fungal skin infection can be up to 6 months.
- Diagnosis of fungal skin infection can be done by skin scraping and examining it under a microscope with 20% KOH.
- Fungal culture may be needed, especially to make specific treatment based on the organism itself. In case of severe infection, a blood culture is required to make sure the infection hasn’t spread to the bloodstream.
- Rarely, if microscopic examination fails, a skin biopsy is needed.
Important Red Flags in Lichen Planus
Although lichen planus is a self-limited disease usually with no complications, it can be a sign of early cancer, so it’s important to see a dentist or a doctor for examination. It’s rare, but 1 to 2 patients who have lichen planus can develop lip, tongue, or mouth cancer. This risk is very minimal in cutaneous lichen planus, though.
Erosive lichen planus in the mouth can be very hard to differentiate from cancer, especially if ulceration is present in the mouth, so referral is important.
