Knee pain is a very common condition that many of us suffer from. Older people and athletes often experience knee pain. But before delving into the details of knee pain, we should have an overview of the knee joint.
The knee joint is a complex joint in our body and is a type of hinge joint. It includes different bones, muscles, ligaments, and menisci.
Bones: The knee joint is composed of the femur, tibia, fibula, and patella.
Ligaments: The knee joint has the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), and lateral collateral ligament (LCL). These ligaments are crucial for the knee joint as they provide stability and support to the joint.
Muscles: The knee joint is surrounded by two main groups of muscles: hamstrings and quadriceps.
The knee joint is also composed of bursae that contain fluid which minimizes the friction of bones and tendons during movements.
Causes of Knee Joint Pain:
There are various causes of knee pain, but the most common causes are:
Trauma/injury: Any trauma or injury to any component of the knee joint can cause knee pain. As we know, the knee joint is made up of muscles, bones, menisci, and ligaments. If there is an injury to any of these parts, your knee will hurt. It includes fractures, sprains, and tears.
Arthritis: It is a prevalent cause of knee pain, especially in females. Osteoarthritis causes damage to the cartilages of the knee joint. Rheumatoid arthritis causes inflammation and damage to the synovial membrane.
Tendinitis and bursitis: Inflammation of tendons and/or bursae of the knee joint can lead to inflammation, swelling, and pain in the knee joint.
Runner’s knee: It is also called patellofemoral pain syndrome. It is most common cause of knee pain in athletes. The patients suffer from persistent dull pain in front of the knee joint (patella). It is basically due to two main reasons.
i. Overuse and stress of the knee during running and other athletic activities.
ii. There is a misalignment of muscles and tendons of the knee joint, which causes inflammation, swelling, and then pain.
Other related symptoms of knee pain include swelling, stiffness, difficulty walking, instability during walking, and clicking sounds.
Diagnosis:
It depends on the medical history, patient’s presentation, X-rays, MRI, CT scan, and blood tests.The imaging techniques are very useful to check for the details and depth of the pathology. The doctor should look carefully to exclude the causes of knee joint pain. As we have discussed several causes of knee pain, doctors should try their best to correctly diagnose the exact cause of knee pain.
Treatment:
It mainly depends on the cause of knee joint pain. It commonly includes bed rest, NSAIDs, steroids, physical therapy for effective rehabilitation. It is also advised to minimize the stress on the knee. Surgery is indicated when there is severe damage of bursae, minisci or other compoments. Some lifestyle modifications are also necessary like reduce weight, and wear proper footwears.
You are advised to follow the instructions of the doctor for effective treatment and recovery.
Contents
- 1 Knee Pain Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How To Recognize Which Disease Is Causing Knee Pain
- 2.1 How to Recognize if Osteoarthritis is Causing Knee Pain
- 2.2 How to Recognize if Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome is Causing Knee Pain
- 2.3 How to Recognize if Chondromalacia Patella is Causing Knee Pain
- 2.4 How to Recognize if Iliotibial Band Syndrome is Causing Knee Pain
- 2.5 How to Recognize if Meniscal Tear is Causing Knee Pain
- 2.6 How to Recognize if Rheumatoid Arthritis is Causing Knee Pain
- 2.7 How to Recognize if Osgood-Schlatter Disease is Causing Knee Pain
- 3 Red Flags With Knee Pain
- 4 Our Additional Resources:
Knee Pain Differential Diagnosis Table:
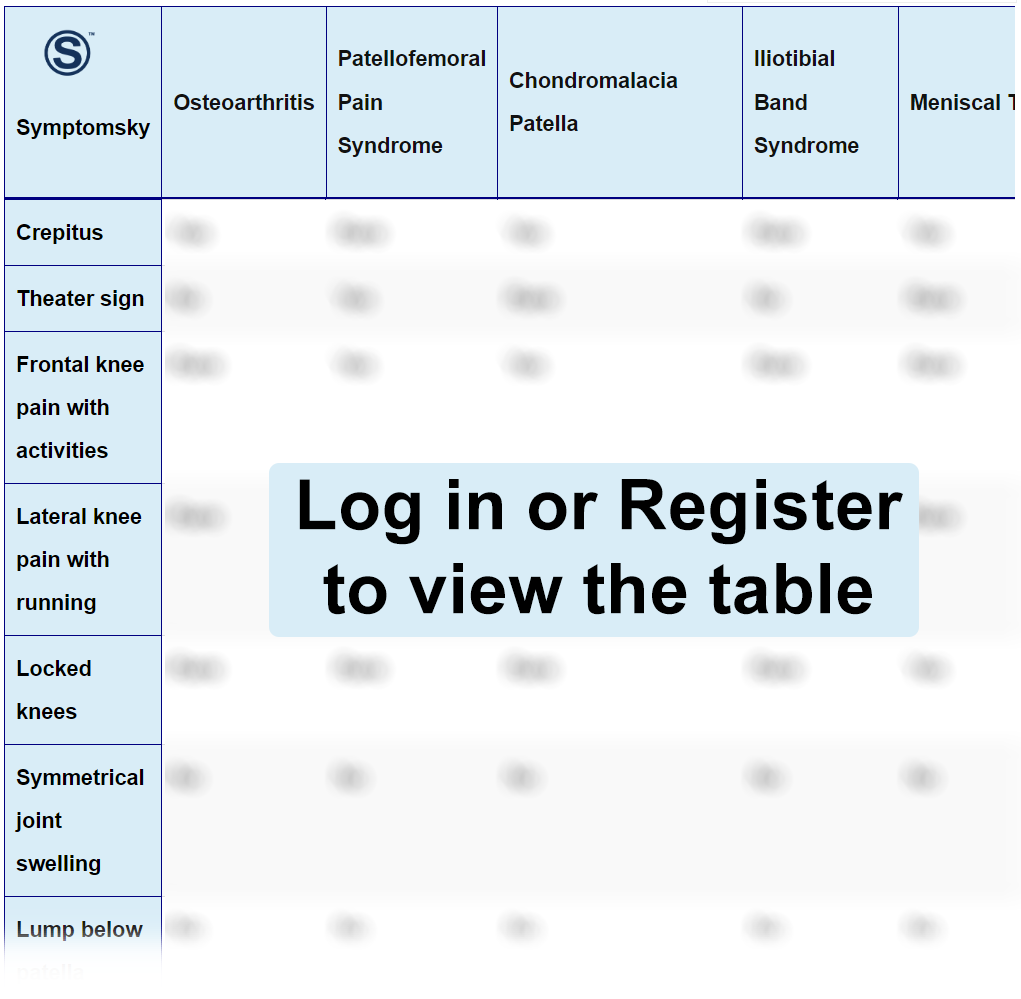
This is some sort of discomfort in the knee most often associated with general wear and tear of knee structures such as cartilage, from daily activities like bending, standing, and lifting. People who do intense exercise like jumping and running are also likely to develop knee pain. The most common causes are related to age, injury, or stress on the knee joint.
There are majorly two types of knee pain: acute knee pain and chronic knee pain. Acute knee pain is a sudden knee pain that accompanies an injury or trauma and is usually sharp, intense, and localized. It is most commonly associated with ligament injury. Chronic knee pain, on the other hand, persists for an extended time and can gradually get worse over time and affect larger areas of the knee.
Pain can be experienced in different parts of the knee to signify different conditions of the knee.
- Pain behind the knee may be caused by tendinitis, a baker’s cyst, or a PCL injury.
- Pain on the lateral side of the knee may indicate iliotibial band syndrome, an LCL injury, a meniscal problem, or osteoarthritis.
- Pain on the medial side of the knee can be caused by an MCL injury, a meniscus problem, or osteoarthritis.
- Pain on the knee cap or the front of the knee can result from an impact, patellofemoral pain syndrome, or osteoarthritis.
Knee pains require proper diagnostics including X-rays and MRI in order to determine the cause of the knee pain and provide the basis for a proper treatment plan. Physiotherapy management can also be essential in management..
How To Recognize Which Disease Is Causing Knee Pain
How to Recognize if Osteoarthritis is Causing Knee Pain
Osteoarthritis is wear and tear of the articular cartilage in the knee. Pain is mostly experienced all around the knee, mostly when trying to move around. The pain is usually accompanied by stiffness of the joint, swelling in the joint, and weakness in the thigh muscles. The pain is mainly felt in three areas of the knee, including the lateral side, the medial side, and the knee cap.
How to Recognize if Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome is Causing Knee Pain
Pain caused by patellofemoral pain syndrome is usually concentrated in the knee cap. It occurs mostly when you are active and after sitting for long with the knees bent. The pain may be accompanied by rubbing, grinding, or clicking of the knee cap when bending or straightening the knee. The knee cap may also be tender to touch..
How to Recognize if Chondromalacia Patella is Causing Knee Pain
Chondromalacia patella is usually the breakdown of the cartilage beneath the knee cap when the knee cap rubs against the thigh bone. Knee pain experienced in this condition is usually located at the front, around, or behind the knee cap. The pain is usually dull and aching and can sometimes worsen with certain movements..
How to Recognize if Iliotibial Band Syndrome is Causing Knee Pain
This is a common knee condition that usually presents with pain and tenderness on palpation of the lateral aspect of the knee, superior to the joint line and inferior to the lateral femoral epicondyle. It is often associated with weakness of the hip abductor muscles.
How to Recognize if Meniscal Tear is Causing Knee Pain
This is a common type of damage to the cartilage in the knee found between the bones in the knee. It is most commonly caused by trauma to the knee. The pain in the knee joint is usually in the medial side, lateral side, and the back of the knee. There is also swelling, catching or locking of the knee, and inability to fully extend or bend the knee..
How to Recognize if Rheumatoid Arthritis is Causing Knee Pain
Rheumatoid arthritis is a type of arthritis where the body’s own immune system attacks the tissues lining the joints. Pain in RA usually affects both the knees and is usually accompanied by stiffness in the morning lasting for 30 minutes, warmth around the joints, swelling, fatigue, malaise, fever, and weight loss.
How to Recognize if Osgood-Schlatter Disease is Causing Knee Pain
This is an inflammation of the area just below the knee where the tendon from the knee cap attaches to the shinbone. The knee pain is usually specified at the tibial tuberosity just below the knee cap. The pain typically lasts a few months but sometimes persists until the teenager has finished growing. This means that in some cases it can last up to two years.
Red Flags With Knee Pain
Many knee problems are a result of the aging process and continual wear and tear on the joint. Other knee problems are a result of injury or strains to the knee.
Common knee problems include: Sprained or strained knee ligaments and/or muscles. A sprained or strained knee ligament or muscle is usually caused by a blow to the knee or a sudden twist of the knee. Symptoms often include pain, swelling, and difficulty in walking. Torn cartilage. Trauma to the knee can tear the menisci (pads of connective tissue that act as shock absorbers and also enhance stability). Cartilage tears can often occur with sprains. Tendonitis. Inflammation of the tendons may result from overuse of a tendon during certain activities such as running, jumping, or cycling. Arthritis. Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis that affects the knee. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative process where the cartilage in the joint gradually wears away. Rheumatoid arthritis can also affect the knees by causing the joint to become inflamed and by destroying the knee cartilage.
Our Additional Resources:
About our project:
Click on the the chat icon in the lower right corner of the screen

Other useful videos about knee pain:
