Contents
- 1 Infectious Mononucleosis Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How to Distinguish Infectious Mononucleosis from Other Infections
- 2.1 Distinguish Cytomegalovirus from Infectious Mononucleosis – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Streptococcal Pharyngitis from Infectious Mononucleosis – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish HIV Infection from Infectious Mononucleosis – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish Influenza from Infectious Mononucleosis – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Adenovirus Infection from Infectious Mononucleosis – Diagnosis
- 2.6 Distinguish Candidiasis from Infectious Mononucleosis – Diagnosis
- 2.7 Distinguish Coxsackievirus Infection from Infectious Mononucleosis – Diagnosis
- 2.8 Distinguish Rubella from Infectious Mononucleosis – Diagnosis
- 3 Important Red Flags with Infectious Mononucleosis
Infectious Mononucleosis Differential Diagnosis Table:
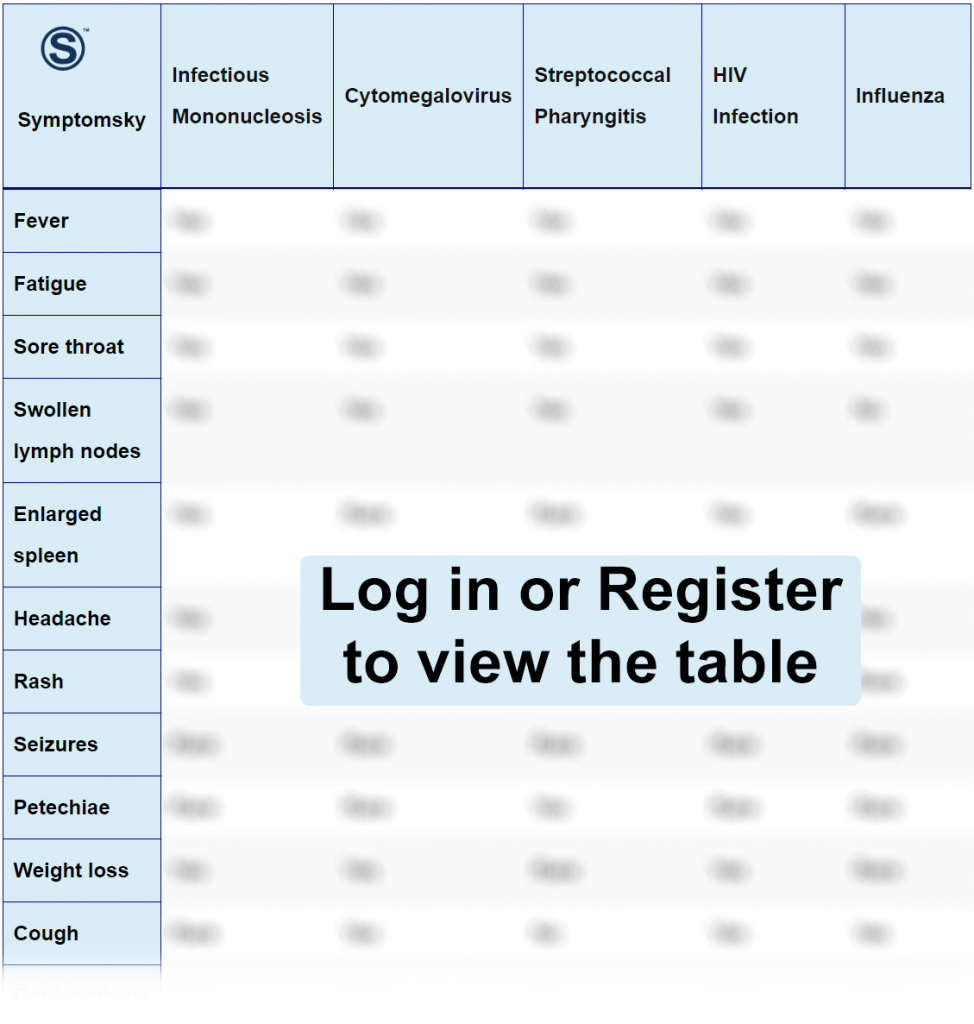
Commonly called mono, this is a viral disease often caused by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), which is a type of herpesvirus called herpes virus 4, mostly spread through kissing. The incubation period for infectious mononucleosis is usually 30-50 days. Most often in children below 5 years, it rarely shows imminent symptoms.
The major symptoms of infectious mononucleosis include extreme fatigue, fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. Generally, the symptoms begin with malaise and slowly progress with fever. Not all 4 symptoms can be present at the same time. Diagnosis is usually done through blood tests and physical examination. Swollen lymph nodes usually suggest an infection.
Blood tests done usually include heterophile antibody or monospot test. A complete blood count can also be done to determine the characteristics of mononuclear white blood cells. There is no specific treatment for infectious mononucleosis but often begins with an initial period of rest, some pain relievers, and some corticosteroids. Fluids can also be given.
How to Distinguish Infectious Mononucleosis from Other Infections
Distinguish Cytomegalovirus from Infectious Mononucleosis – Diagnosis
This is a herpesvirus infection transmitted through sexual or non-sexual contact with blood secretions with a wide range of symptoms involving the eyes, brain, and other internal organs.
- CMV is caused by cytomegalovirus, a herpesvirus type 5, while infectious mononucleosis is caused by Epstein-Barr virus, a herpesvirus type 4.
- CMV is tested using blood tests like PCR or serological tests.
- CMV affects all ages while infectious mononucleosis is more common in teenagers and young adults.
Distinguish Streptococcal Pharyngitis from Infectious Mononucleosis – Diagnosis
Also known as strep throat. This is an infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes causing a sore or a scratchy throat.
- Infectious mononucleosis is caused by Epstein-Barr virus while streptococcal pharyngitis is caused by Streptococcus pyogenes.
- Mono is diagnosed through blood tests while strep throat is diagnosed through a rapid strep test or throat culture.
- Mono affects mostly teenagers and young adults while strep throat affects people of all ages.
Distinguish HIV Infection from Infectious Mononucleosis – Diagnosis
This is an infection that attacks the human body’s immune system, more precisely the CD4 T-lymphocytes, making it weaker and more susceptible to infections.
- HIV is caused by the HIV virus while Mono is caused by Epstein-Barr virus.
Distinguish Influenza from Infectious Mononucleosis – Diagnosis
This is an infection of the respiratory system consisting of the nose, throat, and lungs caused by influenza virus.
- Influenza is caused by influenza virus while mono is caused by Epstein-Barr virus.
- Diagnostic tests for influenza include rapid influenza test and PCR for influenza.
Distinguish Adenovirus Infection from Infectious Mononucleosis – Diagnosis
These are infections that develop from contracting the different types of adenoviruses. They may result in specific syndromes including mild respiratory infections, keratoconjunctivitis, gastroenteritis, cystitis, and primary pneumonia.
- Diagnostic tests such as blood tests for specific antibodies and viral DNA can help differentiate the two.
- Mono is associated with Epstein-Barr virus while adenovirus infections are associated with different types of adenoviruses.
- Mono is associated with symptoms like sore throat, fever, and swollen lymph nodes while adenovirus infections are associated with respiratory and GIT symptoms.
Distinguish Candidiasis from Infectious Mononucleosis – Diagnosis
This is a fungal infection caused by Candida with the most associated species believed to be Candida albicans. Symptoms depend on the location but might include dysphagia, vaginal manifestation, lesions, etc.
- Diagnosis is done by culture examination for candidiasis while blood tests are done for mono.
- Candidiasis is a fungal infection while Mono is a viral infection.
Distinguish Coxsackievirus Infection from Infectious Mononucleosis – Diagnosis
Coxsackie virus infections are a series of infections caused by coxsackie virus which is a member of the enterovirus family. HFMD with ulcers in a child’s mouth and blisters on the hands and feet are the most common infections caused by coxsackie virus.
- Diagnosis of coxsackie virus involves laboratory tests like viral cultures and PCR on samples while diagnosis of mono involves blood tests for EBV-associated antibodies.
Distinguish Rubella from Infectious Mononucleosis – Diagnosis
This is a contagious viral infection best known by its distinctive red rash.
Also called German measles.
Diagnosis involves throat culture and blood testing to differentiate from mono.
Important Red Flags with Infectious Mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis presents with definite signs and symptoms including severe fatigue, high fever, swollen lymph nodes, and a sore throat.
Specific blood tests and a thorough examination are required to diagnose infectious mononucleosis, and treatment begins immediately.
