Contents
- 1 Hypersensitivity Angiitis Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How to Distinguish Bullous Pemphigoid from Other Diseases
- 2.1 Distinguish Viral Exanthem from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Vasculitis from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Other Vasculitis from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish Rheumatoid Arthritis from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Systemic Lupus Erythematosus from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
- 2.6 Distinguish Polyarteritis Nodosa from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
- 2.7 Distinguish Thrombocytopenic Purpura from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
- 2.8 Distinguish Schamberg Disease from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
- 2.9 Distinguish Benign Pigmented Dermatosis from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
- 3 Hypersensitivity Angiitis Red Flags and Treatment
Hypersensitivity Angiitis Differential Diagnosis Table:
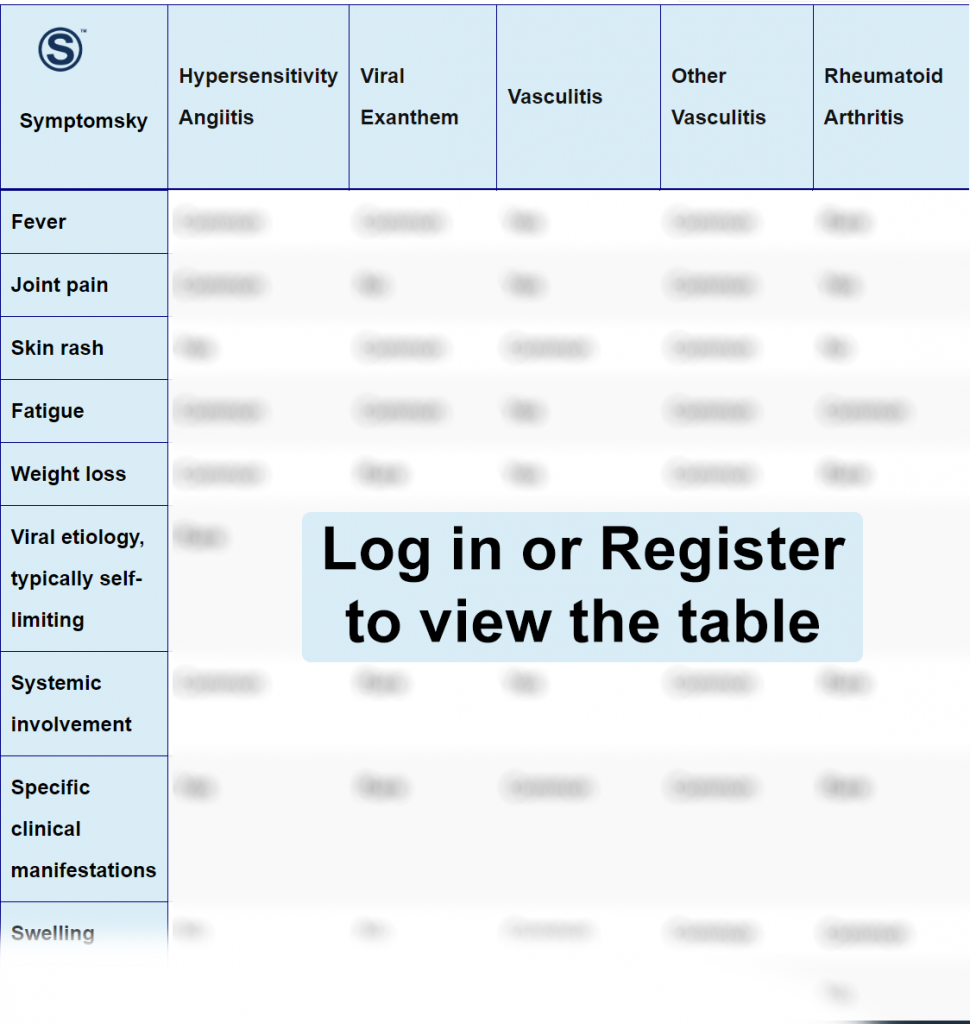
Hypersensitivity angiitis is known as hypersensitivity vasculitis (HV). It is an inflammation in the small blood vessels. Hypersensitivity vasculitis appears on the skin as palpable purpura dominant in the lower extremities. Direct immunofluorescence of a shave skin biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosis, which will show the presence of neutrophils and immune-complex-mediated bodies.
How to Distinguish Bullous Pemphigoid from Other Diseases
Distinguish Viral Exanthem from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
Viral exanthem is a benign rash due to viral infection.
- Viral exanthems appear as red lesions starting from the face and spreading to the body, but hypersensitivity angiitis appears only on lower extremities.
- Viral exanthem appears as pink and red lesions, but hypersensitivity angiitis appears as purple lesions.
“Immunofluorescence, viral swab, and PCR are used for differentiation.”
Distinguish Vasculitis from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
Vasculitis is a broad condition indicating inflammation of blood vessels, including small, medium, and large blood vessels.
“Skin biopsy is used for differentiation between vasculitis and hypersensitivity angiitis.”
Distinguish Other Vasculitis from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
Other types of vasculitis are a secondary cause of disease such as leukemia, lymphoma, hepatitis B, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc.
- Other vasculitis lesions appear as red patches with urticaria, which is absent in hypersensitivity angiitis.
“Skin biopsy and clinical examination are used for differentiation.”
Distinguish Rheumatoid Arthritis from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory autoimmune condition that affects body joints symmetrically.
- Rheumatoid arthritis causes swelling of joints and is characterized by morning stiffness, but hypersensitivity angiitis does not involve morning stiffness.
- Rheumatoid arthritis does not affect the skin, but hypersensitivity angiitis is purple lesions appear on the skin of lower extremities.
“Ultrasound and MRI are used for differentiation between rheumatoid arthritis and hypersensitivity angiitis.”
Distinguish Systemic Lupus Erythematosus from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
Systemic lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune multisystem chronic disease.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus appears as a butterfly rash on the face after sun exposure. Systemic lupus erythematosus also appears as red patches all over the skin, but hypersensitivity angiitis appears as palpable purpura in lower extremities.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus is accompanied by urticaria, yet urticaria is absent in hypersensitivity angiitis.
“X-ray and Blood tests are used for differentiation.”
Distinguish Polyarteritis Nodosa from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
Polyarteritis nodosa is a systemic condition affecting many organs; it is a result of viral infection such as hepatitis B or C.
“Skin biopsy and Liver function lab tests are used for differentiation.””
Distinguish Thrombocytopenic Purpura from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
Thrombocytopenic purpura is an autoimmune disease where platelets are destroyed.
- Thrombocytopenic purpura is located anywhere on the skin, unlike hypersensitivity angiitis, which appears on lower extremities.
“Platelet count blood test is used for differentiation.”
Distinguish Schamberg Disease from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
Schamberg disease is a benign condition.
- Schamberg disease appears as pin-sized purpura lesions with a pigmented base (yellow, red, or brown), but hypersensitivity angiitis appears as purple lesions without pigmentation.
- Schamberg is asymptomatic, but hypersensitivity angiitis is tender and painful.
“Dermascope is used for differentiation.”
Distinguish Benign Pigmented Dermatosis from Hypersensitivity Angiitis – Diagnosis
Benign pigmented dermatosis is a chronic cutaneous eruption characterized by red to purple patches.
- Benign pigmented dermatosis is asymptomatic with no systemic manifestations, while hypersensitivity angiitis is painful with systemic manifestations.
“Dermascope and skin biopsy are used for differentiation.”
Hypersensitivity Angiitis Red Flags and Treatment
Untreated Hypersensitivity angiitis causes severe ulceration.
Most idiopathic HV patients’ symptoms are self-limiting and completely resolve when the offending agent is diminished. Comprehensive management is helpful, such as antihistamines, resting, leg elevation, and compressions. In persistent or resistant cases, a four to six-week corticosteroid tapered dose is suggested. In cases where HV is a secondary cause, if HV is drug-induced, diminishing the drug is crucial; if HV is a secondary cause of infection, the infection must be treated.
