Contents
- 1 Human Immunodeficiency Virus Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How to Distinguish HIV from Other Diseases
- 2.1 Distinguish Influenza from HIV – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Acute Retroviral Syndrome from HIV – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Mono from HIV – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish CMV Infection from HIV – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Chronic Fatigue Syndrome from HIV – Diagnosis
- 2.6 Distinguish Tuberculosis from HIV – Diagnosis
- 2.7 Distinguish Hepatitis B from HIV – Diagnosis
- 2.8 Distinguish Toxoplasmosis from HIV – Diagnosis
- 2.9 Distinguish Syphilis from HIV – Diagnosis
- 2.10 Distinguish Lymphoma from HIV – Diagnosis
- 3 Important Red Flags with HIV
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Differential Diagnosis Table:
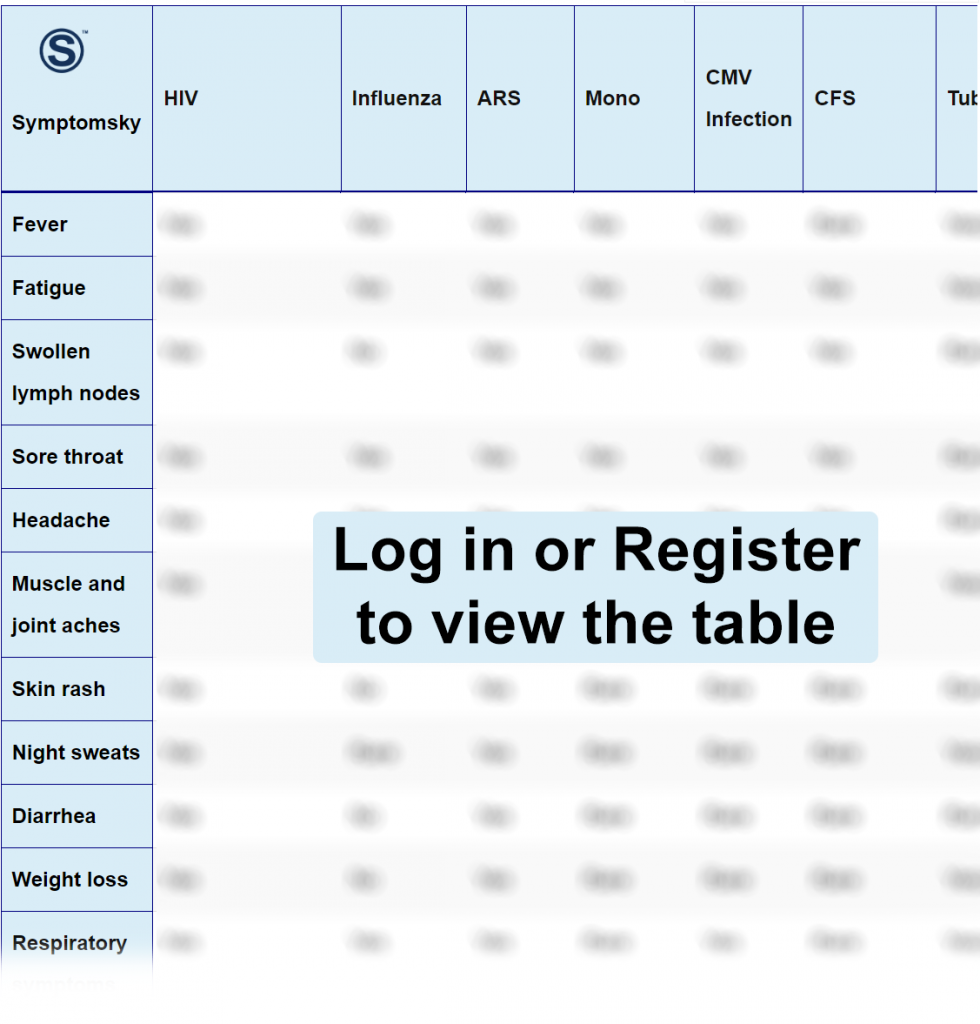
This is a blood-borne virus usually transmitted via the exchange of body fluids with an infected individual, attacking cells in the body, making it more vulnerable to other infections and diseases. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is the most advanced stage of the disease.
HIV is a member of the retroviruses and can be caused by either HIV-1 or HIV-2, with HIV-1 as the most dominant one. When HIV enters the body, it releases its RNA, then a DNA copy is made by the enzyme transcriptase. It destroys a certain type of white blood cells called the CD4+ lymphocytes.
At the initial stages of infection, symptoms are usually not noticeable but may start to develop within 1-4 weeks. Some of the symptoms may include fever, rashes, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, white patches on the mouth due to candidiasis, shingles, progressive loss of weight, anemia, and diarrhea.
How to Distinguish HIV from Other Diseases
Distinguish Influenza from HIV – Diagnosis
This is a flu. It’s an acute respiratory illness/infection caused by the influenza virus with symptoms like body aches, fever, cough, and other symptoms of respiratory distress. It can cause mild to severe illness and sometimes lead to death.
- Influenza is transmitted through respiratory droplets while HIV is transmitted through the exchange of bodily fluids with an infected person.
- HIV symptoms might be unnoticeable for a sometimes, while influenza symptoms are imminent from the point of infection.
- HIV is a retrovirus while influenza is a respiratory virus.
- HIV attacks CD4+ lymphocytes weakening the immune system, making the body susceptible to other diseases, while influenza attacks the respiratory system.
This is the first stage of infection with HIV, and their symptoms are similar to those of the flu and do disappear on their own after a few weeks. They include headache, nausea, diarrhea, and body aches.
Distinguish Mono from HIV – Diagnosis
Also called mononucleosis or the kissing disease. This is an infection caused by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) usually found in the saliva.
- Testing for mononucleosis is done through the Monoclot test or specific antibody tests for EBV.
- Mononucleosis is caused by EBV while HIV is caused by the retroviruses HIV-1 or HIV-2.
Distinguish CMV Infection from HIV – Diagnosis
This is the cytomegalovirus infection. This is an infection by a type of herpes virus with a wide range of symptoms from fever and fatigue to severe symptoms involving the eyes, brain, or other internal organs. The virus is spread through sexual and non-sexual contact with body secretions.
- CMV can be detected via culture, serologies, antigen assays, polymerase chain reaction, and cytopathology.
- CMV is a herpes virus while HIV is a retrovirus.
- HIV mainly attacks CD4+ lymphocytes weakening the immune system while CMV has a wide cell tropism, infecting a variety of cell types.
Distinguish Chronic Fatigue Syndrome from HIV – Diagnosis
This is a disease characterized by blood pressure and heart rate regulation problems, profound fatigue, sleep abnormalities, pain, and other symptoms made worse by exertion. It’s more common in women but can affect anyone, including children.
- Diagnosis of CFS is majorly based on the symptoms and their causes since there is no single test to diagnose it.
- CFS lacks a known viral cause while HIV is a retroviral disease caused by HIV-1 or HIV-2.
- CFS is majorly characterized by body fatigue while HIV has a wide range of symptoms.
Distinguish Tuberculosis from HIV – Diagnosis
This is an infectious disease usually caused by bacteria, and it majorly affects the lungs.
- Diagnosis of TB may involve Mantoux tuberculin skin test, Interferon-gamma release assay for Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- TB is caused by bacteria while HIV is caused by a retrovirus.
- TB is transmitted through the air while HIV is transmitted through the exchange of bodily fluids.
- TB majorly affects the respiratory system while HIV affects the immune system specifically CD4 cells.
Distinguish Hepatitis B from HIV – Diagnosis
This is an infection of the liver caused by the Hepatitis B virus, which is commonly transmitted via body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions.
- Serological tests, thorough examination, abdominal ultrasonography, CT, and MRI can be used to diagnose Hepatitis B.
- Hepatitis B virus belongs to the hepadnaviridae family while HIV belongs to the retroviridae family.
- Hep B primarily affects the kidney while HIV attacks the immune system.
- Hep B contains DNA as its genetic material while HIV contains RNA as its genetic material.
Distinguish Toxoplasmosis from HIV – Diagnosis
This is an infection by a parasite called Toxoplasma gondii, which reproduces in the intestinal tracts of cats, and humans can become infected by direct or indirect contact with cat poop or eating undercooked meat.
- Testing is done by Immunoglobulin testing, brain biopsy, lumbar puncture, lymph node biopsy, amniocentesis, and bronchoalveolar lavage.
Distinguish Syphilis from HIV – Diagnosis
Syphilis is an infectious bacterial disease caused by Treponema pallidum and is transmissible by sexual contact with infectious lesions or via blood transfusion.
- Serological testing is considered the standard method of detection for all stages of syphilis.
Distinguish Lymphoma from HIV – Diagnosis
This is a cancer that forms in the germ-fighting lymphatic cell. There are two main types, namely Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- CBC, examination, and biopsy can be used to diagnose lymphoma.
Important Red Flags with HIV
HIV is asymptomatic and can hardly be noticeable in the early stages. Blood tests can also give negative results.
HIV has different stages of development, and if not well managed at an early stage, it can progress to more severe stages of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS).
HIV weakens the immune system of an individual, making them more susceptible to different diseases like TB.
