Contents
- 1 Esophagitis Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 Differentiating Esophagitis From Other Conditions
- 2.1 Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disorder (GERD)
- 2.2 Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Peptic Ulcer
- 2.3 Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Esophageal Motility Disorder
- 2.4 Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Eosinophilic Esophagitis
- 2.5 Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Barrett’s Esophagus
- 2.6 Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Esophageal Cancer
- 2.7 Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Infectious Esophagitis
- 2.8 Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Medication-Induced Esophagitis
- 2.9 Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Mallory-Weiss Tear
- 2.10 Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Achalasia
- 3 Red Flags with Esophagitis
Esophagitis Differential Diagnosis Table:
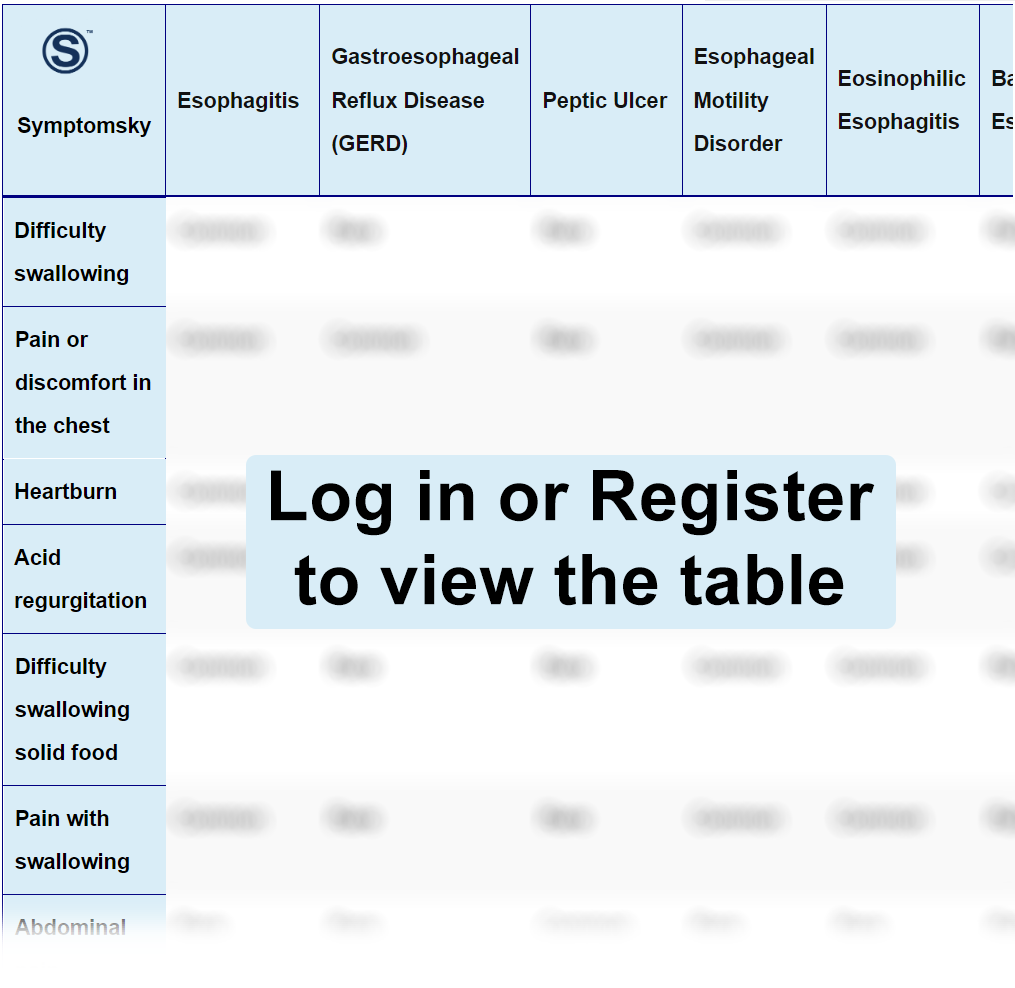
This is basically inflammation of the inner lining of the esophagus, which is the tube that carries food through the chest, from the mouth to the stomach. The inflammation is usually due to a number of factors, but the major causes of esophagitis include gastro-esophageal reflux disorder (GERD), which is the major cause. It involves the backflow of digestive acid to the esophagus, causing a burning effect on the esophagus.
The major forms of esophagitis include reflux esophagitis, infectious esophagitis, pill esophagitis, and eosinophilic esophagitis. Other causes include eating disorders, some medications (e.g., aspirin, doxycycline, NSAIDs), chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer, and certain infections like candidiasis and CMV. Symptoms include difficult or painful swallowing, acid reflux, heartburn, chest pain, nausea, and vomiting.
Bleeding can also be seen as blood in vomit or darkening of stool. Diagnosis is majorly done through endoscopy and esophageal biopsy. A barium X-ray can also be conducted. Treatment of esophagitis is dependent on the causes but majorly involves modification of activities, prescription of antacid drugs, and sometimes surgery to strengthen valves separating the esophagus and stomach..
Differentiating Esophagitis From Other Conditions
Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disorder (GERD)
This is where stomach contents, e.g., bile and digestive acid, flow backward into the esophagus from the stomach, causing inflammation in the esophagus..
- Endoscopy in GERD is used to estimate the extent of damage on the esophagus while it’s a diagnostic procedure in esophagitis.
- Esophagitis is caused by many other factors apart from acid reflux while GERD is mainly caused by acid reflux.
GERD causes esophagitis..
Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Peptic Ulcer
This is a sore in the lining of the stomach or duodenum..
- Peptic ulcer is usually caused by Helicobacter pylori bacteria.
- Esophagitis develops in the lining of the esophagus, while peptic ulcer develops in the lining of the stomach or duodenum.
- PH monitoring is essential in the diagnosis of esophagitis, while it’s not that essential in the diagnosis of GERD..
Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Esophageal Motility Disorder
Esophageal motility disorder is a dysfunction of the esophagus making it hard for food to move or rather swallow, causing chest pain and heartburn.
- Esophagitis is mainly diagnosed through endoscopy while esophageal motility disorder can be diagnosed using esophageal manometry.
- Esophageal motility disorder is a defect of the function of esophageal muscles making them hard to contract normally while esophagitis involves inflammation..
Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Eosinophilic Esophagitis
This is a chronic inflammatory disorder triggered by food allergies in which the wall of the esophagus becomes filled with large numbers of eosinophils, which is a type of white blood cell..
- Diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis is done by determining the eosinophil count, while esophagitis is generally done by endoscopy to determine the cause.
- Eosinophilic esophagitis is not usually related to acid reflux..
Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Barrett’s Esophagus
Barrett’s esophagus is a complication of GERD where the normal esophageal squamous epithelium is converted to metaplastic columnar epithelium, a tissue similar to that of the intestines.
- Esophagitis shows signs of inflammation, erosions, or ulcers, while Barrett’s esophagus endoscopy reveals specialized intestinal cells in the esophageal lining.
- Barrett’s esophagus is a premalignant condition predisposing to the development of esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Esophageal Cancer
This is a type of cancer that develops in the esophagus usually when abnormal cells start growing in an uncontrolled way in the esophagus/food pipe..
- Blood tests in esophagitis might show the presence of inflammatory markers while blood tests in esophageal cancer show elevated tumor markers.
- Endoscopic ultrasound can be used in diagnosing esophageal cancer as it assists in staging the cancer.
Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Infectious Esophagitis
Infectious esophagitis basically means inflammation of the esophagus caused by an infection like bacterial, fungal, or viral infection. Diagnosis of infectious esophagitis involves microbiological cultures to determine the cause.
Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Medication-Induced Esophagitis
Medication-induced esophagitis is the destruction of the mucosal lining of the esophagus through different kinds of medications. Antibiotics such as doxycycline, and gelatin capsules are common causes of pill esophagitis.
Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Mallory-Weiss Tear
Mallory Weiss tear is the tear of the tissue of the lower esophagus due to violent coughing and vomiting. It can start to bleed.
- Esophagitis is the inflammation of the esophageal lining while Mallory Weiss is a longitudinal tear of the inner esophageal lining.
- Endoscopy reveals the tear.
- Mallory Weiss is characterized by hematemesis and melena.
Differentiating Between Esophagitis and Achalasia
Achalasia is a rare swallowing disorder that affects the esophagus, usually believed to be caused by degeneration of nerve cells located between the layers of esophageal muscles.
Red Flags with Esophagitis
Esophagitis has a wide range of presentations; therefore, thorough diagnostic procedures need to be taken in order to come up with a clear diagnosis and proper treatment plans. However, some signs may signify an underlying infection:
- Dysphagia.
- Odynophagia.
- Weight loss.
- Anemia.
- Melena.
- Hematemesis.
- History of smoking and alcohol intake.
