Contents
- 1 Epidermomycosis Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How To Distinguish Epidermomycosis from Other Diseases
- 2.1 Distinguish Atopic Dermatitis from Epidermomycosis – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Contact Eczema from Epidermomycosis – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Psoriasis from Epidermomycosis – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish Seborrheic Dermatitis from Epidermomycosis – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Tinea Infection from Epidermomycosis – Diagnosis
- 2.6 Distinguish Pityriasis Rosea from Epidermomycosis – Diagnosis
- 2.7 Distinguish Cutaneous Candidiasis from Epidermomycosis – Diagnosis
- 2.8 Distinguish Granuloma Annulare from Epidermomycosis – Diagnosis
- 3 Important Red Flags of Epidermomycosis
Epidermomycosis Differential Diagnosis Table:
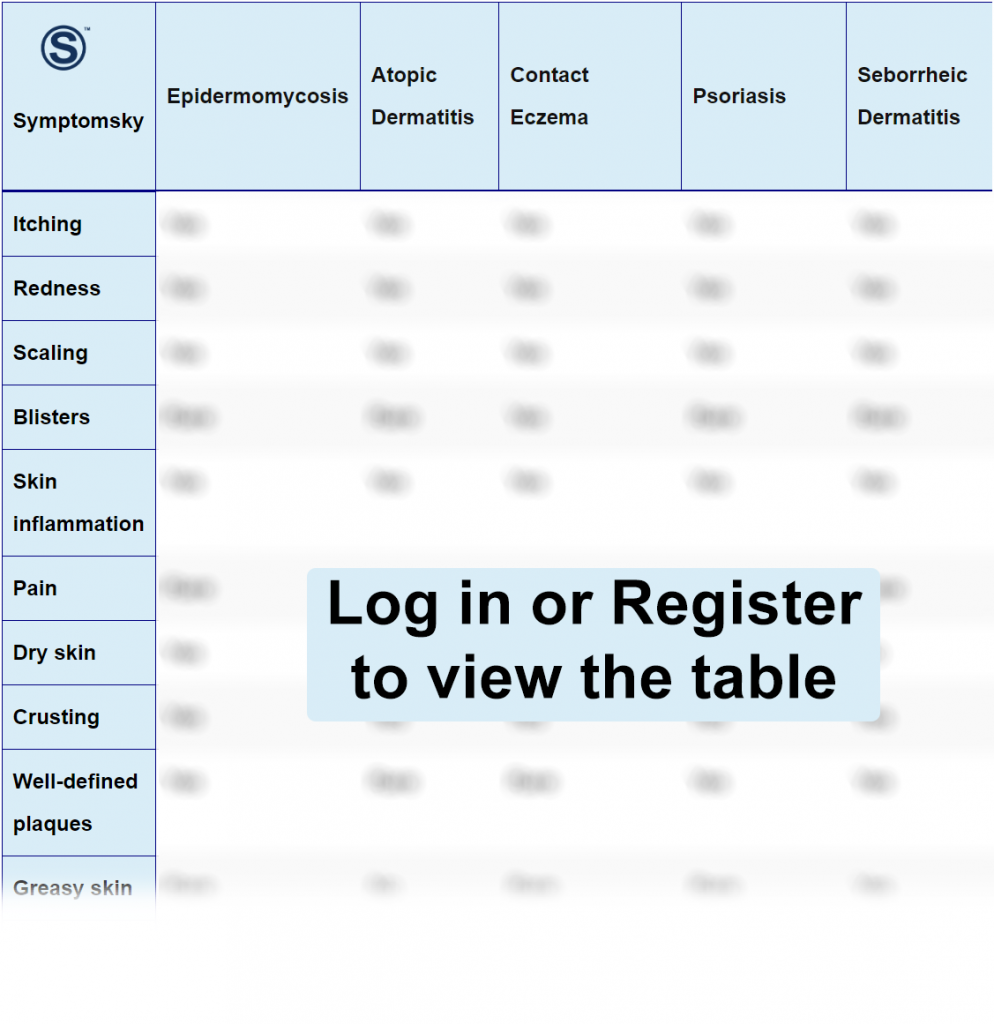
Epidermomycosis is a self-limited, superficial fungal infection that affects the epidermis. It usually affects the epidermis of hairless skin, large folds, soles of feet, and palms of the hand. Symptoms include painless, red, scaly, ring-shaped, and itchy rash with crusts on it.
It is caused by dermatophytes. Dermatophytes usually affect the epidermis of the skin, nails, and hair. Dermatophytes that involve the stratum corneum of the skin are called epidermomycosis.
It spreads by person-to-person contact, skin-to-skin contact, or using belongings of the infected person like sharing towels, sharing shaving kits, common bathtubs, swimming pools, etc.
Epidermomycosis is diagnosed on history and examination of the lesion, while culture can also be performed. It is a self-limiting disease, but treatment with antifungal is required.
How To Distinguish Epidermomycosis from Other Diseases
Distinguish Atopic Dermatitis from Epidermomycosis – Diagnosis
Atopic Dermatitis is a long-lasting disease of the skin caused by irritants, allergens, infections, or certain environmental factors. Symptoms of atopic dermatitis are itchy, dry, discolored rash on the skin that may ooze or crust and make the skin hard. The features which distinguish atopic dermatitis from epidermomycosis are;
- Atopic dermatitis is caused by allergies, certain environmental factors, stress, and anxiety while Epidermomycosis is a fungal infection caused by dermatophytes.
- Atopic dermatitis causes dry, itchy, and scaly patches of skin while epidermatomycosis causes reddish, itchy ring-shaped rash with hair loss on the affected area.
- Atopic Dermatitis isn’t contagious while epidermomycosis is highly contagious.
It is diagnosed on history, clinical examination, blood tests, or biopsy. Daily moisturization, Corticosteroid creams, and medication with phototherapy are helpful in treatment.
Distinguish Contact Eczema from Epidermomycosis – Diagnosis
Contact Eczema is a non-contagious itchy rash caused by contact with an irritant or an allergic substance. It causes a red, dry, itchy, and flaky rash on white skin, while itchy hyperpigmented patches on dark skin. These patches sometimes show inflammation, oozing, and crusting. The features that distinguish contact eczema from epidermomycosis are;
- Contact Eczema is caused by contact with a certain irritant and the body’s immune response to certain triggers while epidermomycosis is caused by fungus.
- Contact Eczema is a non-communicable disease while epidermomycosis can spread through person-to-person contact or contact with infected belongings of the infected person.
- Contact dermatitis can be present anywhere on the body where the skin comes in contact with the causative agent while epidermomycosis usually affects the epidermis where two skin surfaces come in contact with each other.
Contact eczema is diagnosed on history, examination, and patch testing. Anti-allergic, anti-itch creams, and medicines along with the avoidance of irritants are helpful in treatment.
Distinguish Psoriasis from Epidermomycosis – Diagnosis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, autoimmune skin disease. It appears as an itchy, discolored patch with greyish or silvery-white scales that can appear anywhere in the body, but knees, elbows, lower back, and the scalp are more prone to develop psoriasis. The features that distinguish psoriasis from epidermomycosis:
- Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease while epidermomycosis is a fungal manifestation of the skin.
- Psoriasis has plaques with silvery-white scales while epidermomycosis has reddish, circular, or ring-shaped rash.
- Psoriasis is mainly present on knees, elbows, lower back, and the scalp though it can appear anywhere on the body while epidermomycosis develops on hairless skin, interigo, palms, and soles.
Psoriasis is diagnosed clinically but skin biopsy can be performed for confirmation of diagnosis. Treatment options are topical and oral corticosteroids with phototherapy has proven effective.
Distinguish Seborrheic Dermatitis from Epidermomycosis – Diagnosis
Seborrheic Dermatitis is a common skin condition which usually affects areas where the skin is oily due to the presence of sebaceous glands. It appears as itchy, white and greasy scales or flakes (dandruff) on the scalp, eyebrows, beard, hairs, ears, chest, armpits, folds of the breast, and the groin region. The features which distinguish seborrheic dermatitis from epidermomycosis are:
- Seborrheic dermatitis is mainly present on areas where there is excess sebum production; mainly on the scalp and face while epidermomycosis appears on areas with humidity.
- Although it is hard to differentiate, the former doesn’t cause hair loss or broken hairs while epidermomycosis appears on hairless skin or can cause hair loss.
- Seborrheic dermatitis has oily or greasy skin while epidermomycosis has dry skin.
It is usually diagnosed on clinical examination but skin biopsy can also be performed. Dandruff shampoos, antifungal medications, and corticosteroids are helpful in treatment.
Distinguish Tinea Infection from Epidermomycosis – Diagnosis
Tinea Infection or Ringworm is a communicable disease caused by fungal infection. It is found in warm and moist parts of the body such as the scalp, groin, underarms, beneath the breast, and feet. Symptoms of tinea are; ring-shaped, itchy rash having red, scaly, and cracked skin. The features which distinguish tinea from epidermomycosis are;
- Tinea is a fungal infection that can be present on the scalp, groin, underarms, feet, and beneath the breast while epidermomycosis affects the epidermis outside the intertrigo.
- Although both tinea and epidermomycosis belong to the same class of dermatomycoses, the difference is tinea can be present anywhere while tinea of hairless skin is epidermomycosis.
Tinea is diagnosed on the history and clinical examination of the lesion. Antifungal medicines are used for the treatment of tinea infection.
Distinguish Pityriasis Rosea from Epidermomycosis – Diagnosis
Pityriasis rosea is a papulosquamous viral infection. It forms large, red, circular or oval-shaped, mildly raised patches (Herald Patch) on the body. Less common symptoms include headache, fatigue, arthralgias, or flu-like symptoms. The features which distinguish Pityriasis rosea from epidermomycosis are;
- Pityriasis rosea is caused by the herpes virus while epidermomycosis is a fungal infection caused by dermatophytes.
- Although both are self-limiting, pityriasis rosea resolves in about 6 weeks to 10 weeks and it isn’t contagious while epidermomycosis is highly contagious but resolves in one week.
- Pityriasis Rosea develops a typical Christmas tree rash, especially on the face, back, and trunk, and rarely on other parts of the body, while epidermomycosis is present less commonly on these parts.
Pityriasis rosea is diagnosed on clinical examination of its typical rash. Furthermore, skin biopsy is also helpful. It usually doesn’t require treatment, but antihistamines and moisturizers are helpful in relieving symptoms.
Distinguish Cutaneous Candidiasis from Epidermomycosis – Diagnosis
Cutaneous Candidiasis is a yeast infection caused by Candida albicans. It develops as an itchy, red, and inflamed rash with mildly raised pustules or bumps, and white patches on the tongue and oral cavity are also found. It usually affects skin areas that are warm and moist. The features which distinguish cutaneous candidiasis from epidermomycosis are;
- Both diseases, due to their similar clinical presentation, are often hard to differentiate, but cutaneous candidiasis causes a more severe infection and affects people who are immunocompromised or using immunosuppressive drugs.
- Cutaneous Candidiasis is usually non-contagious, but epidermomycosis is contagious.
- Cutaneous Candidiasis has a bright red flat rash with a freckled appearance while epidermomycosis has a red circular rash.
It is diagnosed through clinical examination, biopsy, and culture. Antifungal medications are used for treatment.
Distinguish Granuloma Annulare from Epidermomycosis – Diagnosis
Granuloma Annulare is a benign, self-limiting skin disorder. Symptoms are small, smooth, annular, raised, discolored rash or bumps with a normal or depressed center. The features which distinguish granuloma annulare from epidermomycosis are;
- Granuloma annulare is thought to be a delayed hypersensitivity reaction, although the exact cause is still unknown, while epidermomycosis is a fungal infection.
- Granuloma annulare develops painful bumps while epidermomycosis is usually painless.
- Although both conditions are self-limiting, the former usually persists from months to years while the latter resolves in a week.
- Both lesions are ring-shaped, but granuloma annulare can be normal or depressed from the center while epidermomycosis spreads from the center to the periphery.
Granuloma Annulare is diagnosed through clinical examination, but skin biopsy can also be performed. It is usually treated with corticosteroid creams, lotions, and intralesional steroid injections.
Important Red Flags of Epidermomycosis
- Although epidermomycosis is a self-limiting condition, it is highly contagious. Any rash that persists for more than 2 weeks needs urgent medical help.
- Epidermomycosis can affect any individual, but people with low immunity are more prone to infection and take more than the usual time for healing.
- Epidermomycosis usually doesn’t leave a scar, but rarely it goes deeper into the skin and leaves bad scars that take time to go away or need dermatologist help.
