Contents
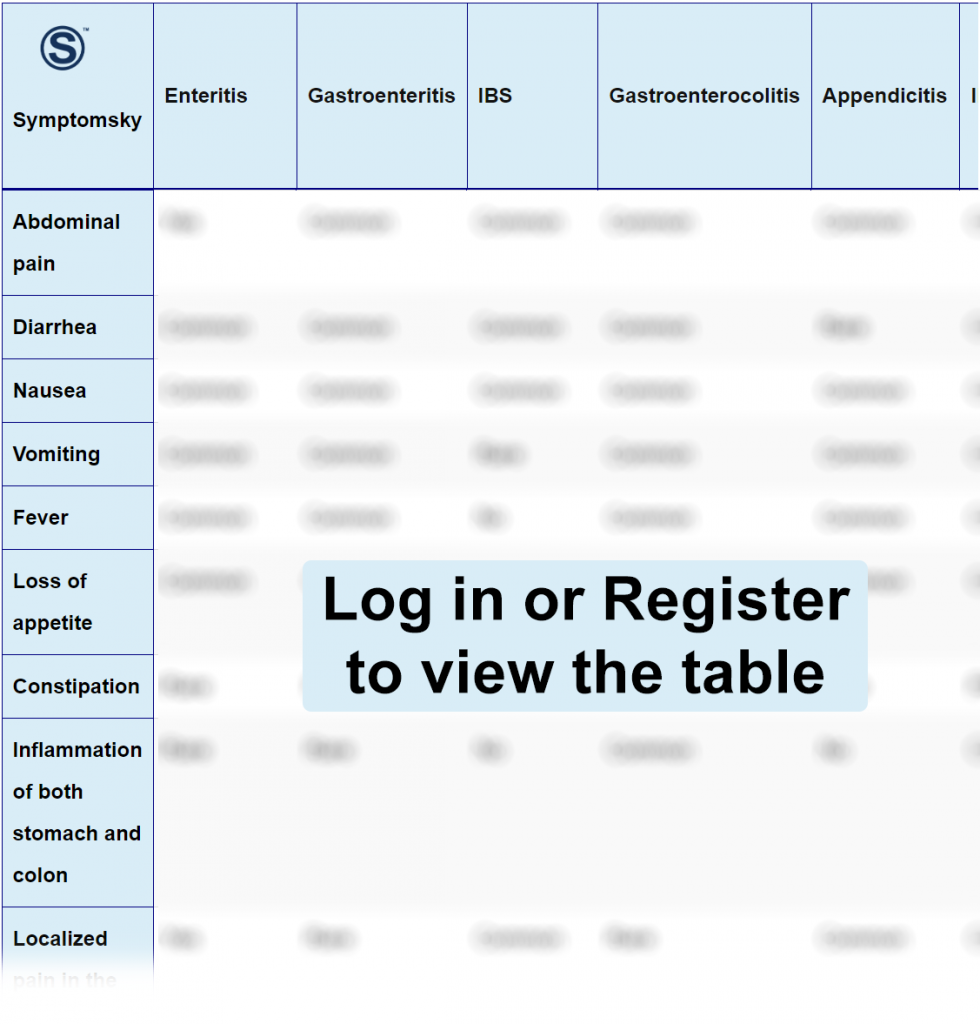
Enteritis Differential Diagnosis Table:
The gastrointestinal tract is a passage between the mouth and anus. This tract helps to ingest food and removes waste products from the body. There are many diseases that can affect this tract, and ultimately the normal functions are disrupted.
Enteritis is a condition affecting the small intestine specifically. It is a common condition that produces inflammation of the small intestine.
The common symptoms include abdominal pain and discomfort, bowel disruption, nausea, vomiting, fever, loss of appetite, blood, or mucous discharge in the stool.
How To Distinguish Enteritis from Other Diseases
Distinguish Gastroenteritis from Enteritis – Diagnosis
Gastroenteritis is an inflammation of the stomach along with the small intestine. So, all the enteritis symptoms are present in gastroenteritis, and differentiation is not possible.
- Gastroenteritis produces pain in the stomach region, which is not common in enteritis.
- Radiation and chemotherapy-induced enteritis may cause bowel obstruction leading to constipation. However, constipation is uncommon in gastroenteritis.
Distinguish IBS from Enteritis – Diagnosis
IBS or irritable bowel syndrome is a chronic condition that affects the gastrointestinal tract. It produces repeated pain in the abdomen and changes in bowel movements.
- IBS is a chronic condition, and symptoms persist for a longer duration. However, most cases of enteritis are induced by an infection, so they usually heal within days.
- Enteritis usually presents with fever, a rare finding in IBS.
- IBS can produce diarrhea and constipation. However, in enteritis, diarrhea is common, but constipation is a rare finding.
“IBS diagnosis criteria are the presence of symptoms like abdominal pain and bowel changes for over three months. This does not apply to enteritis.”
Distinguish Gastroenterocolitis from Enteritis – Diagnosis
Gastroenterocolitis is an inflammation of the stomach, large, and small intestine.
- Enteritis pain is only present in the lower right abdomen region, while gastroenterocolitis pain can be anywhere in the region of the stomach and intestines.
“On the abdominal CT scan, abdominal wall thickening can be seen in the small intestine only. While, in gastroenterocolitis, it can also be seen in the colon.”
Distinguish Appendicitis from Enteritis – Diagnosis
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix.
- Appendicitis pain usually starts in the center of the belly around the belly button and moves to the lower right corner. However, enteritis pain is centered at the lower right corner only.
- Appendicitis pain usually starts as a dull pain and then gradually becomes so intense that it is difficult to tolerate. While the appendicitis pain is severe from the beginning and subsides quickly.
“On palpation, rebound tenderness is positive for appendicitis, but it is rare to be found in enteritis.”
Distinguish IBD from Enteritis – Diagnosis
IBD or inflammatory bowel disease comprises two conditions: ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
- IBD is actively involved in unexplained weight loss. It is uncommon in enteritis.
- Mucus in stool is another common finding with IBD which is rare in enteritis.
- Blood in stool is common in IBD and it is not present in enteritis.
“On clinical examination, IBD patients show signs of rebound tenderness which are not seen in enteritis patients.”
Common Red Flags With Enteritis
Enteritis is not a fatal condition, and it is possible to manage it at home with rest and medication. The common red flags include excessive vomiting, diarrhea, blood in stools, and unintended weight loss. Dehydration can occur as a result of excessive vomiting and diarrhea. Another aspect to consider is blood in stool, as it is not common in enteritis and may suggest some other serious conditions like IBD or hemorrhoids. Unintended weight loss is also not a common condition with enteritis, and it is associated with other serious conditions like IBD and cancer.
