Contents
- 1 Dyshidrosis Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How To Distinguishing Dyshidrosis From Other Diseases
- 2.1 Distinguish Scabies From Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Pustular Psoriasis from Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Epidermomycosis from Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish Eczema from Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Tinea Pedis from Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
- 2.6 Distinguish Herpes Simplex from Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
- 2.7 Distinguish Contact Dermatitis from Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
- 2.8 Distinguish Impetigo from Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
- 2.9 Distinguish Pemphigus from Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
- 3 Important Red Flags of Dyshidrosis
Dyshidrosis Differential Diagnosis Table:
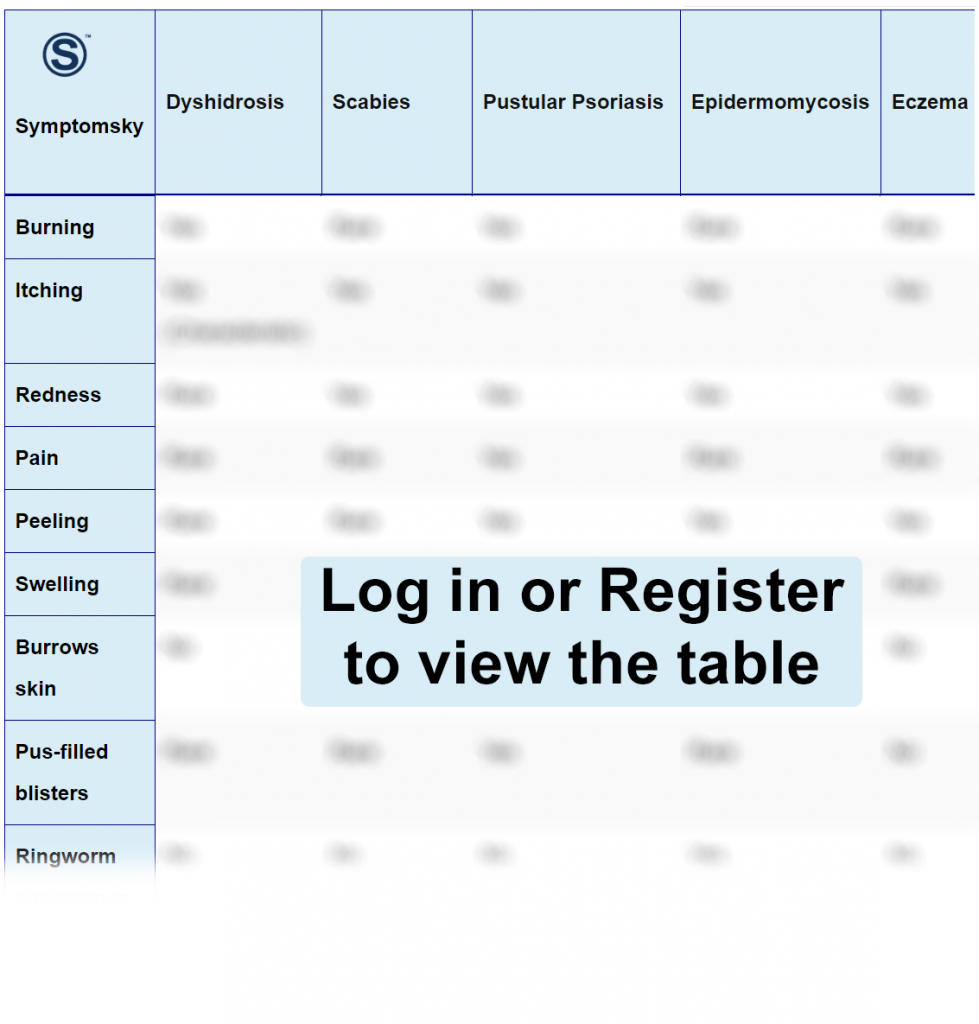
Dyshidrosis is a type of chronic skin eczema. Symptoms of dyshidrosis are small, dry, itchy, and scaly patches of skin with blisters on palms, soles, and sides of fingers. These blisters can cause severe itching, redness, cracked skin, and crusting of blisters.
The cause of dyshidrosis is idiopathic but it is found to be in association with certain factors like irritants and an allergic reaction to metals, fungal infection, photosensitivity to light, smoking, and use of OCPs.
It is thought to be caused in people who lack a protein, Filaggrin. Filaggrin is responsible for building a strong and protective skin barrier.
It is diagnosed based on history and examination of the blisters. Patch tests, blood tests, or biopsies can also be performed. There is no definite cure for this disease, but corticosteroid creams and moisturization can help in relieving the symptoms.
How To Distinguishing Dyshidrosis From Other Diseases
Distinguish Scabies From Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
Scabies is a communicable disease caused by a severe itch-causing mite called Sarcoptes scabiei. Symptoms are intense itching and a severe itchy rash. The features that differentiate scabies from dyshidrosis are:
- Sometimes, scabies and dyshidrosis are hard to differentiate because of their similar rash, but the former is a contagious disease while the latter is a non-contagious disease.
- Scabies is caused by a mite that forms burrows in the skin, while dyshidrosis is caused by an irritant or an allergen.
- In scabies, itching flares up mostly at night, while dyshidrosis can flare up anytime.
- The rash of scabies is mostly present on finger webs and private parts, while dyshidrosis rash is present on palms, soles, and sides of fingers.
Scabies is diagnosed based on history, clinical examination, and visualization of skin scraping under a microscope. Permethrin 5% and 0.5 malathion lotion are used for the treatment of scabies.
Distinguish Pustular Psoriasis from Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
Pustular Psoriasis, as the name suggests, is an uncommon, inflammatory, and chronic variant of psoriasis vulgaris and can be present anywhere on the body. Symptoms include dry, scaly, reddish or discoloured skin having fluid or pus-filled blisters/pustules. Less common symptoms are temperature with chills, headache, dehydration, and tachycardia. The features that distinguish Pustular Psoriasis from Dyshidrosis are:
- In Pustular Psoriasis, vesicles contain pus, while dyshidrosis has fluid-filled vesicles.
- Pustular Psoriasis is an immune-related disease and can affect the quality of life, while Dyshidrosis is not an autoimmune disease.
- Pustular Psoriasis can be present anywhere in the body, while dyshidrosis is usually present on palms, soles, and sides of fingers.
History and physical examination can help in diagnosis, but KOH preparations and biopsy can also be performed. Treatment can help in relieving the symptoms, but there is no definite cure for this disease.
Distinguish Epidermomycosis from Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
Epidermomycosis is a rare infection of the epidermis layer (stratum corneum) of the skin caused by dermatophytes. Causative agents for this disease are yeasts and molds. The features that distinguish them from dyshidrosis are:
- Epidermomycosis is caused by a fungal infection while dyshidrosis is caused by an irritant or an allergen.
- Epidermomycosis is presented as a ring-shaped papule that is inflamed and spreads peripherally, while Dyshidrosis presents as symmetrical, tiny vesicles that vary in size and shape.
- Epidermomycosis papules are mostly painless, while dyshidrosis is quite painful and itchy.
Epidermomycosis is diagnosed on history, clinical examination, blood tests, and culture can also be performed. It is treated with antifungal medications.
Distinguish Eczema from Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
Eczema is a skin disease that weakens the skin barrier, making the skin more susceptible to irritants or an allergen. It causes non-communicating dry and itchy rash or bumps on the skin that sometimes can turn into thick, flaky, scaly, or crusty skin. The features that distinguish eczema from dyshidrosis are:
- Eczema can be present anywhere, but more prone sites are hands, feet, neck, ankles, knees, elbows, face, and lips while dyshidrosis is limited to palms, soles, and sides of fingers.
- Eczema is usually painless but causes pain on scratching while dyshidrosis has painful and itchy blisters.
- Dyshidrosis is a type of eczema which is found commonly in females.
It is usually diagnosed with naked eyes while skin biopsy, patch test, and blood test are also helpful in diagnosis. Daily moisturization, oral and topical steroids, immunosuppressant, and antihistamine are used for treatment.
Distinguish Tinea Pedis from Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
Tinea Pedis or Athlete’s foot is a contagious disease caused by a fungal (dermatophytes) infection on the feet. It causes discolored, ring-shaped, itchy, dry, scaly, and cracked skin between fingers or feet that often peel off. Blisters can also form with a burning sensation on the skin. The features which distinguish Tinea Pedis from dyshidrosis are:
- Tinea pedis is a fungal infection while dyshidrosis is caused by an irritant or an allergen.
- Tinea pedis can spread through using common swimming pools, showers, locker rooms, and contact with a person or its belongings who have tinea pedis while dyshidrosis is non-contagious.
- Tinea Pedis is localized to toes and feet while dyshidrosis is more widespread; it is present on hands, feet, and sides of the fingers.
Tinea pedis is diagnosed on history and examination of the lesion while KOH preparations can also be helpful. Antifungal treatment is recommended for this disease.
Distinguish Herpes Simplex from Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
Herpes Simplex is a contagious disease caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV). Type 1 HSV causes painful ulcers and blisters in or around the mouth, while Type 2 HSV causes genital ulcers and sores. The features which distinguish herpes simplex from dyshidrosis are:
- Herpes Simplex spreads through skin-to-skin contact or by sexual contact while dyshidrosis doesn’t show this type of spread.
- Herpes simplex develops painful blisters near the fingernails while dyshidrosis has blisters on palms, soles, and sides of the fingers which become painful in severe disease.
- Herpes simplex virus can remain latent for a lifetime while dyshidrosis sometimes shows a relapsing and remitting pattern.
It is diagnosed through viral culture, PCR, and blood tests. This disease doesn’t have a cure, but antivirals can be used to reduce the severity and ease the symptoms.
Distinguish Contact Dermatitis from Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
Contact Dermatitis, as the name suggests, is caused by contact with an irritant, specific substance, or an allergic reaction to it. Symptoms are itchy rashes, hyperpigmented patches, bumps, and blisters that cause dry, flaky, and cracked skin. The features which distinguish contact dermatitis from dyshidrosis are:
- Contact Dermatitis rash appears where the skin comes in contact with a specific irritant or substance while dyshidrosis eczema can occur bilaterally.
- Contact Dermatitis has clear and specified borders while dyshidrosis rash can vary in size and shape.
- Contact Dermatitis can be both acute and chronic but is mostly acute while dyshidrosis is a chronic condition.
Contact Dermatitis is diagnosed based on history and clinical examination while patch tests or clinical examinations can also be performed. Contact Dermatitis is treated with steroid creams and ointments.
Distinguish Impetigo from Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
Impetigo is a skin infection caused by bacteria; Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. Symptoms include itchy sores that are red in color; the sores burst and ooze. After some days, “honey-colored crust” scabs develop on the sore, which ultimately heals without leaving a scar. The features which distinguish impetigo from dyshidrosis are:
- Impetigo is caused by bacteria that are normal flora of humans but develop an infection when the skin barrier is compromised while dyshidrosis is thought to be caused by an irritant or an allergen.
- Impetigo can occur anywhere on the body but usually affects the face; around the mouth and nose while dyshidrosis affects palms, soles, and sides of fingers.
- Impetigo is highly contagious but it isn’t dangerous while dyshidrosis isn’t contagious.
- The distinguishing point of impetigo is that it forms ‘honey-colored scab’ on sores or blisters while dyshidrosis forms blisters that may be purple or reddish in color with clear fluid.
Impetigo is diagnosed on the examination of the sore while gram staining and culture can help in identifying the bacterial cause. Antibiotic creams and ointments or oral antibiotics are useful in the treatment of impetigo.
Distinguish Pemphigus from Dyshidrosis – Diagnosis
Pemphigus is a rare autoimmune disease of the skin and mucous membrane. Symptoms include painful and fragile fluid-filled blisters present on the mouth, eyes, nose, throat, and genitals. These blisters, when ruptured, form crusted erosions. The features which distinguish pemphigus from dyshidrosis are;
- Pemphigus is an autoimmune disease while dyshidrosis is caused by certain irritants or an allergen.
- Both diseases can be present at any age, but the former is mostly present over the age of forty while the latter is usually present before 40 years of age.
- Pemphigus is present on eyes, nose, mouth, throat, and genitals while dyshidrosis is found on palms, soles, and sides of fingers.
Pemphigus is diagnosed on history, examination of the blisters, blood tests, and biopsy. Treatment options include daily moisturization, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and phototherapy are helpful.
Important Red Flags of Dyshidrosis
Dyshidrosis is a relapsing condition but usually goes away without complications. Sometimes, in severe cases, it is superimposed by bacterial infection, which results in large blisters that spread to the back of hands and feet, which are quite painful, filled with pus, and can delay the healing process. It needs urgent treatment with antibiotics.
