Contents
- 1 Diverticulosis Of Colon Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How To Distinguish Diverticulosis Of Colon from Other Diseases
- 2.1 Distinguish Irritable Bowel Syndrome from Diverticulosis – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Inflammatory Bowel Syndrome from Diverticulosis – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Gastroenteritis from Diverticulosis – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish Appendicitis from Diverticulosis – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Colorectal Polyps from Diverticulosis – Diagnosis
- 2.6 Distinguish Ischemic Colitis from Diverticulosis – Diagnosis
- 2.7 Distinguish Colorectal Cancer from Diverticulosis – Diagnosis
- 2.8 Distinguish Celiac Disease from Diverticulosis – Diagnosis
- 3 Common Red Flags with Diverticulosis
Diverticulosis Of Colon Differential Diagnosis Table:
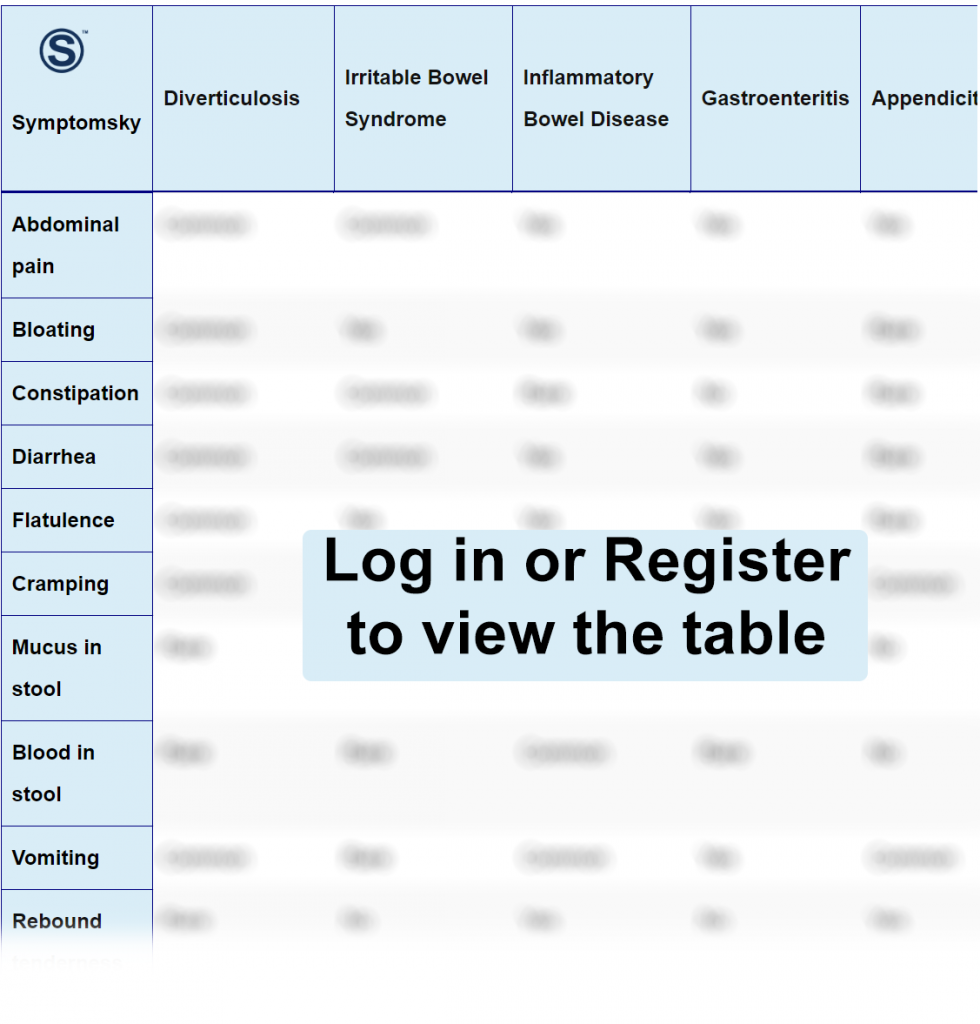
Small pouches or sacs can form along the walls of the digestive tract, most commonly in the lower intestine. These are termed diverticula, and their presence is referred to as diverticulosis. They seldom cause problems and are more common in people over the age of 40.
Diverticulosis normally does not produce symptoms, and people are unaware they have it. They produce symptoms when they get affected either by infection, food waste, or any disease in the vicinity that makes them sensitive. Whenever present, the symptoms are abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, bloating, flatulence, and occasionally rectal bleeding. Mucus in stool and fever are also present in the case of infection.
How To Distinguish Diverticulosis Of Colon from Other Diseases
Distinguish Irritable Bowel Syndrome from Diverticulosis – Diagnosis
Irritable bowel syndrome is a group of symptoms, namely abdominal pain, changes in appearance and frequency of bowel movements, and bloating. The presentation of both diseases seems similar, but they are different based on:
- It has been quoted that irritable bowel disease symptoms improve after defecation. However, diverticulosis pain persists even after having a bowel movement.
- Passing stools with mucus is a very common finding in irritable bowel syndrome. It is a rare finding in diverticulosis and only present when the disease is superimposed by an infection.
- Diverticulosis itself does not produce symptoms normally. They are present when diverticula or diverticulum is superimposed by an infection. In this case, one can notice fever and chills. These symptoms are not common in irritable bowel syndrome.
Distinguish Inflammatory Bowel Syndrome from Diverticulosis – Diagnosis
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammation of the digestive tract and involves two diseases: Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative colitis.
- Diverticulosis and inflammatory bowel disease both produce changes in bowel movements. These include diarrhea and constipation. While diarrhea is common in both of them, constipation is common only in diverticulosis. It can occur in IBD but rarely.
- IBD is known to produce unexplained weight loss. This is a rare finding in diverticulosis.
“On physical examination, both of them are found to be tender to palpation. However, rebound tenderness is present only in inflammatory bowel disease patients.”
Distinguish Gastroenteritis from Diverticulosis – Diagnosis
Gastroenteritis is an inflammation of the stomach and intestine mucosa.
- Constipation is very common in diverticulosis; however, it’s rare to be found in gastroenteritis.
- Diverticulosis is usually present in older individuals, while gastroenteritis is an acute infection that can present in any age group.
- In some cases, diverticulosis may produce bleeding from the rectum, which can be seen in the feces. It’s never seen in gastroenteritis.
Distinguish Appendicitis from Diverticulosis – Diagnosis
The appendix is a pouch-like protrusion on the right side of the colon, and its inflammation is called appendicitis.
- Appendicitis pain is usually very severe and starts suddenly, while diverticulosis pain starts mildly and progresses to intense pain over a matter of days.
- Appendicitis pain worsens with coughing and moving, which is not a common finding in diverticulosis.
- Diverticulosis is frequently associated with bloating and flatulence, which are very rare to be found among appendicitis patients.
“Upon palpation, Rovsing’s sign is positive only for appendicitis, not for diverticulosis. This is positive referred tenderness and rebound tenderness in the lower right quadrant after palpating the quadrant on the opposite side.”
Distinguish Colorectal Polyps from Diverticulosis – Diagnosis
Colorectal polyps are small protrusions along the lining of the large intestine. They are also symptomless and seldom produce symptoms like diverticulosis.
- Abdominal pain is a consistent finding in diverticulosis symptomatic cases. However, in the case of polyps, only large ones produce pain.
- Colorectal polyps actively produce chronic bleeding, which can be seen as streaks of blood in feces. In the case of diverticulosis, rectal bleeding is a rare finding. Moreover, the bleeding in the case of polyps results in iron deficiency anemia, which is not common in diverticulosis.
Distinguish Ischemic Colitis from Diverticulosis – Diagnosis
Ischemic colitis is a consequence of an abrupt cessation of blood flow to the colon resulting in tissue damage.
- The symptoms of ischemic colitis typically appear suddenly within 24 hours. It’s not the case with diverticulosis.
- Constipation is a rare finding in ischemic colitis, while it’s very common in diverticulosis.
Distinguish Colorectal Cancer from Diverticulosis – Diagnosis
Colorectal cancer is the malignant transformation of the cells of the colon and rectum.
- Cancer produces unexplained weight loss, which is uncommon in diverticulosis.
- Cancer can produce adjacent lymph nodes swelling, which never occurs in diverticulosis.
Distinguish Celiac Disease from Diverticulosis – Diagnosis
Celiac Disease is caused by an immune reaction after consuming gluten-containing food items.
- Weight loss is a common finding in celiac disease patients, which is rare to be found among diverticulosis patients.
- Moreover, there is always a history of gluten intolerance in these patients, which is uncommon in diverticulosis patients.
Common Red Flags with Diverticulosis
Diverticulosis is usually symptomless, and generally, people don’t even have any idea that they have it for years. It usually does not cause any serious issues. It can, however, become problematic if it is superimposed by infection, develops an abscess, blocks the intestinal canal, perforates, or develops an abnormal connection with other organs. The red flag symptoms include severe pain in the abdomen, a persistent fever, vomiting, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding. This warrants a hospital visit, and it is an emergency situation.
