Contents
- 1 Congestive Heart Failure Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How to Distinguish Congestive Heart Failure from Other Diseases
- 2.1 Distinguish Myocardial Infarction from CHF – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Pneumonia from CHF – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Pulmonary Embolism from CHF – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish Chronic Kidney Disease from CHF – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Valvular Heart Disease from CHF – Diagnosis
- 2.6 Distinguish Hypothyroidism from CHF – Diagnosis
- 2.7 Distinguish Pericarditis from CHF – Diagnosis
- 3 Important Red Flags with Congestive Heart Failure
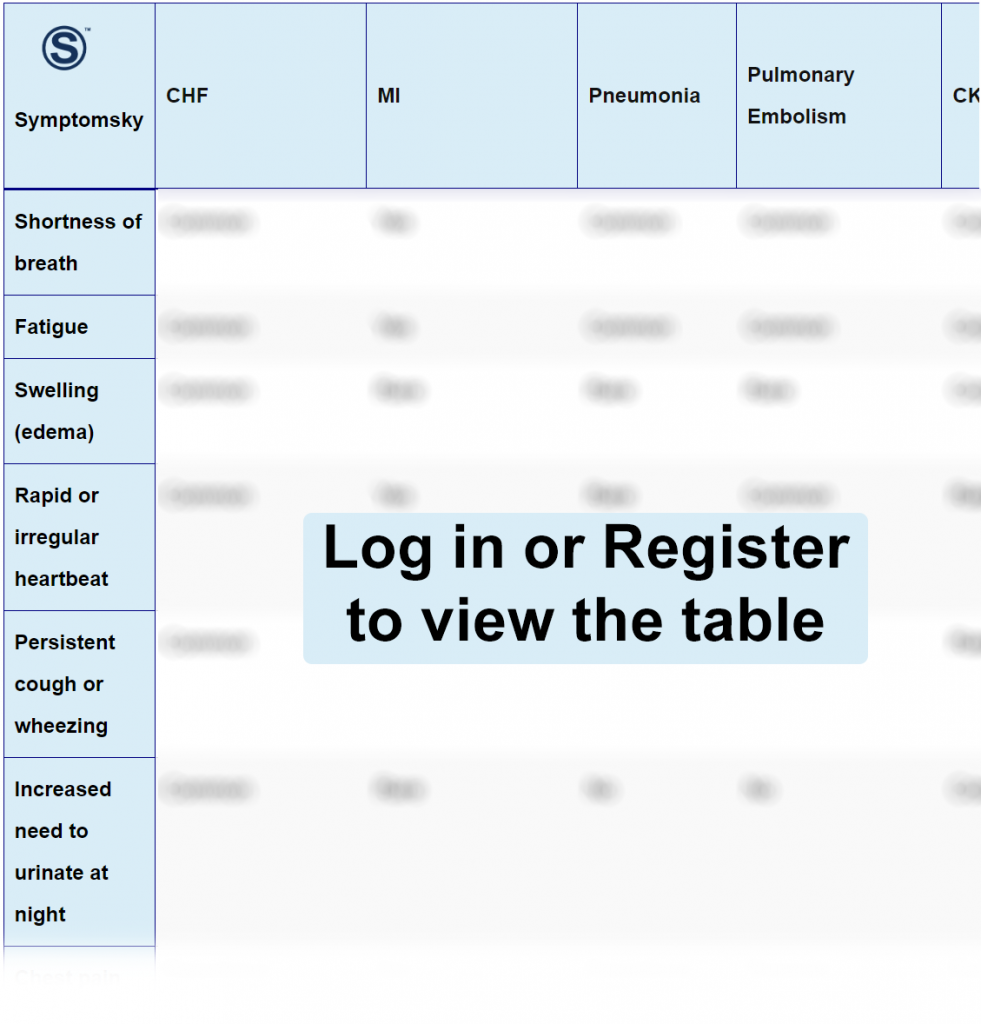
Congestive Heart Failure Differential Diagnosis Table:
This is a chronic condition of the heart where it does not pump blood effectively to meet the body requirements. This does not necessarily mean that the heart has completely failed; it only means that the heart muscles have become too weak to initiate a stronger contraction in order to push blood outside the body at the rate at which it is refilling.
In patients with heart failure, a thorough physical examination is crucial as it is used to guide both diagnosis and management whether inpatient or outpatient. Some additional maneuvers may include measurement of jugular venous pressure, Valsalva maneuver, and hepatojugular reflux as needed.
Presenting symptoms may include dyspnea, peripheral edema, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, and bendopnea. Therapy for CHF is mainly centered on improving the cardiopulmonary physiology of the patient; therefore, a combination of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and slow titration of beta-blocker can be recommended.
How to Distinguish Congestive Heart Failure from Other Diseases
Distinguish Myocardial Infarction from CHF – Diagnosis
Majorly known as a heart attack. This is a situation where there is the formation of plaques in the interior walls of arteries supplying the heart muscles, therefore reducing blood flow to the heart muscles, depriving them of enough oxygen supply.
- Myocardial infarction occurs due to a blood clot in the arteries supplying the heart muscles while CHF is generally the inability of the heart to effectively pump blood.
Myocardial infarction can lead to congestive heart failure.
Distinguish Pneumonia from CHF – Diagnosis
This is an infection that inflames one or both lungs caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses where the air sacs are filled with fluid or pus.
- Pneumonia is a respiratory infection whereas CHF is a cardiovascular condition.
- Swelling mostly in the lower extremities is majorly experienced in CHF due to fluid retention, but not in pneumonia. The only fluid buildup in pneumonia is experienced in the air sacs.
- In pneumonia, the fluid inside the lungs contains white blood cells trying to fight pathogens/infections while in CHF the fluid usually builds up in the lungs is caused by leakage from the lung blood vessels.
Distinguish Pulmonary Embolism from CHF – Diagnosis
Pulmonary embolism refers to a blockage in the blood vessels that transport blood to the lungs, usually by a clot/emboli. The clot usually comes from the deep veins, i.e., in cases of deep venous thrombosis.
- Pulmonary embolism involves a clot in the blood vessels to the lungs while CHF is a defect of the heart.
- Chest pains are more intense and severe in pulmonary embolism while the symptoms in CHF are progressive.
They are both defects of the cardiovascular system; therefore, thorough physical examination and investigations are required.
Distinguish Chronic Kidney Disease from CHF – Diagnosis
This is a condition where the kidneys gradually lose their function and can no longer filter blood as required. This increases the amount of waste in the body.
- Chronic kidney disease affects the kidneys while chronic heart failure affects the heart’s ability to pump blood.
- Obesity and inactivity are major risk factors in the development of CHF while they are not that pronounced in CKD.
CKD can cause CHF and vice versa.
Distinguish Valvular Heart Disease from CHF – Diagnosis
This is damage to a valve of the heart where either the valve does not close completely, allowing backflow of blood, or the valve opening becomes narrow [stenosis].
- Valvular heart disease majorly focuses on the heart valves while CHF is a condition of the heart muscles affecting its ability to pump blood.
Distinguish Hypothyroidism from CHF – Diagnosis
This is a defect of the thyroid gland where it does not produce enough thyroid hormones.
- Hypothyroidism is a defect of the thyroid gland affecting its ability to produce thyroid hormone, affecting the general metabolism of the body while CHF is a defect of the heart affecting its ability to pump blood.
Distinguish Pericarditis from CHF – Diagnosis
Pericarditis is inflammation of the thin outer layer of the heart known as the pericardium, usually caused by viral infections. The specific cause is, however, unknown.
- CHF affects the ability of the heart to pump blood while pericarditis does not.
- Pain in pericarditis sometimes goes away without treatment while CHF is persistent.
Important Red Flags with Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure has a lot of symptoms similar to other conditions; therefore, diagnosis requires a more specific approach in order to make the correct diagnosis.
Some of the red flags include persistent shortness of breath, rapid weight gain, swelling in the lower extremities and the abdomen, and persistent coughing.
