Contents
- 1 Colic Pain Right Upper Quadrant Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How To Recognize Which Disease Is Causing RUQ Colic Pain
- 2.1 How to Recognize if Gallstones are Causing RUQ Colic Pain
- 2.2 How to Recognize if Cholecystitis is Causing RUQ Colic Pain
- 2.3 How to Recognize if Hepatitis is Causing RUQ Colic Pain
- 2.4 How to Recognize if Pancreatitis is Causing RUQ Colic Pain
- 2.5 How to Recognize if Cholangitis is Causing RUQ Colic Pain
- 2.6 How to Recognize if Biliary Atresia is Causing RUQ Colic Pain
- 2.7 How to Recognize if Coledocholithiasis is Causing RUQ Colic Pain
- 3 Common Red Flags WIth RUQ Colic Pain
Colic Pain Right Upper Quadrant
Differential Diagnosis Table:
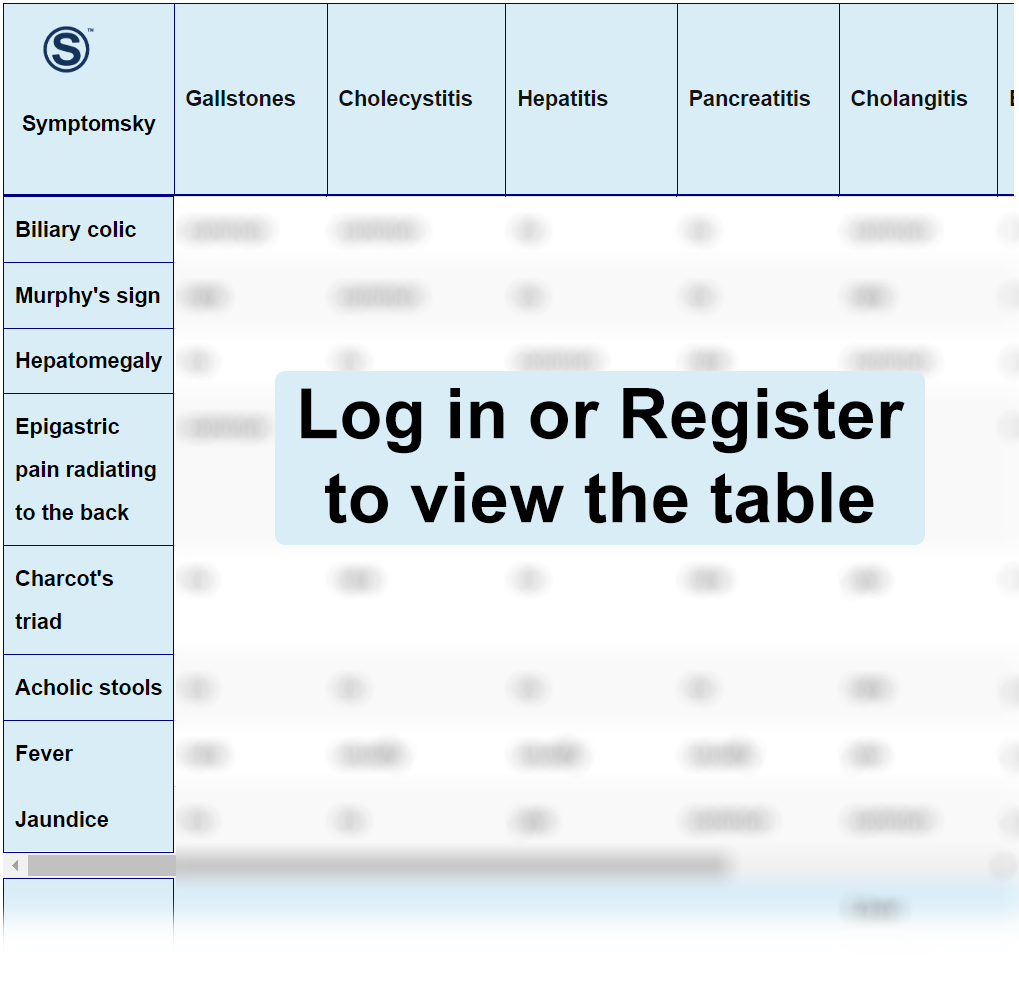
The etiology of abdominal pain is multiple and varied as it can include many diseases and is a frequent reason for consultation in emergency departments. The abdomen can be divided into four quadrants. The right upper quadrant contains different organs such as the liver, gallbladder, pancreatic head, right kidney, and duodenum.
Due to the structures found within this quadrant, the causes of right upper abdominal pain can be numerous. The pain can remain in the quadrant or extend or radiate to other quadrants, even to another region such as the back. Pain can be acute, dull, or aching; these classifications can guide physicians towards a diagnosis. Symptoms that may accompany this pain are nausea, vomiting, fever, constipation or diarrhea, increased tenderness, inflammation, and jaundice. Diagnosis is confirmed by imaging studies, including abdominal ultrasound, abdominal CT scan, abdominal MRI, or MRI cholangiopancreatography, as well as laboratory tests.
How To Recognize Which Disease Is Causing RUQ Colic Pain
How to Recognize if Gallstones are Causing RUQ Colic Pain
Gallstones are stones that originate in the gallbladder or bile duct from solidified substances that exist within the gallbladder. This condition may be asymptomatic and diagnosed by a routine diagnostic test. When symptomatic, it is characterized by pain in the epigastrium that radiates to the right upper quadrant. Pain intensifies after fatty meals, is generally a colicky type of pain, and may present with nausea and vomiting. It is usually more prevalent in women than men.
How to Recognize if Cholecystitis is Causing RUQ Colic Pain
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder. During physical examination, Murphy’s sign test is positive. It may present with vomiting, fever, and chills. It is characterized by intense pain in the right upper quadrant, which becomes more severe after pressing on it during inspiration and releasing the area during expiration. Pain can radiate to the right shoulder. Cholecystitis may be acalculous or calculous, depending on the presence of lithiasis or not, with calculous being more common.
How to Recognize if Hepatitis is Causing RUQ Colic Pain
Hepatitis is a viral infection of the liver that is transmitted through direct contact with blood or other body fluids of an infected person. It is characterized by pain in the right upper quadrant after a flu-like process accompanied by anorexia, fever, arthralgia, vomiting, nausea, choluria, and jaundice.
How to Recognize if Pancreatitis is Causing RUQ Colic Pain
Pancreatitis is the inflammation of the pancreas. The main symptom is a sudden intense pain in the right upper quadrant that radiates to the back and is always accompanied by nausea and vomiting. A very characteristic finding is that the pain is relieved by leaning forward. The patient may also be tachycardic and febrile.
How to Recognize if Cholangitis is Causing RUQ Colic Pain
Cholangitis is a liver disease that produces inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts. These patients present with a triad characterized by right upper quadrant pain, fever, and jaundice. Other symptoms that accompany this triad are pruritus, diarrhea, fatigue, chills, ascites, and gastrointestinal bleeding.
How to Recognize if Biliary Atresia is Causing RUQ Colic Pain
Biliary atresia occurs when the bile ducts become inflamed and blocked and only affects infants. Symptoms appear 2-6 weeks after birth. The patient presents jaundice, abdominal distension, acholic stools, and choluria. The patient may also present splenomegaly and hematemesis.
How to Recognize if Coledocholithiasis is Causing RUQ Colic Pain
It is the presence of stones inside the bile duct. It produces a colicky pain in the right upper quadrant accompanied by jaundice, choluria, and causes general malaise such as fever, chills; it may also cause pancreatitis. It may be asymptomatic.
Common Red Flags WIth RUQ Colic Pain
The majority of patients admitted to the emergency department with right upper quadrant abdominal pain have surgical causes; great care is recommended for these patients.
It is important to avoid the use of analgesics in patients with this pain as it may mask the diagnosis.
It is extremely essential for any female patient of childbearing age who enters the emergency room with this type of pain to rule out pregnancy.
