Contents
- 1 Chronic Obstructive Asthma Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How to Distinguish Chronic Obstructive Asthma from Other Infections
- 2.1 Distinguish Chronic Obstructive Asthma from Asthma – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Chronic Obstructive Asthma from Chronic Bronchitis – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Chronic Obstructive Asthma from Emphysema – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish Chronic Obstructive Asthma from Bronchiectasis – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Chronic Obstructive Asthma from Cystic Fibrosis – Diagnosis
- 3 Important Red Flags with Chronic Obstructive Asthma
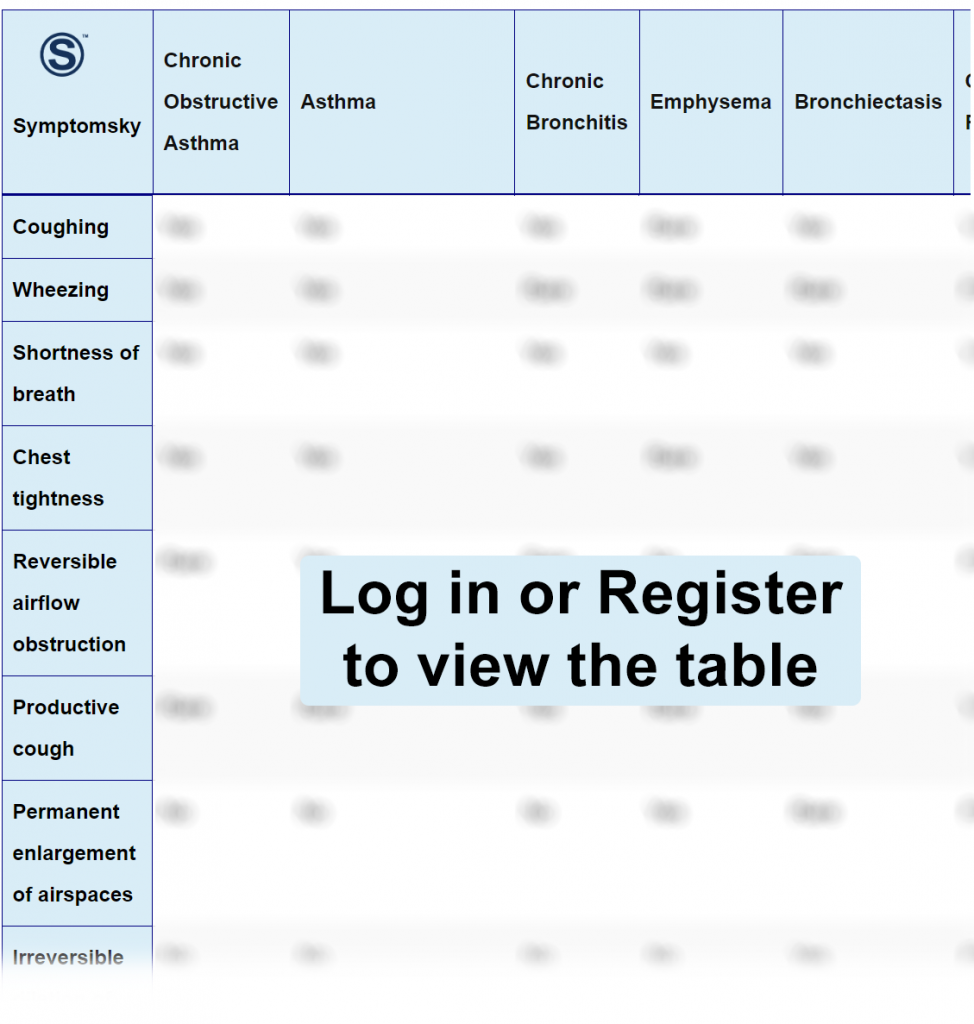
Chronic Obstructive Asthma Differential Diagnosis Table:
This is a chronic respiratory condition developing from a combination of chronic bronchitis and asthma. It causes obstruction of the respiratory system due to regular inflammation of the airways causing them to become narrow. It is closely associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease since their symptoms tend to overlap.
Some of the signs and symptoms of chronic obstructive asthma may include; airway inflammation, increased mucus production, difficulty breathing, wheezing, frequent coughing, excess phlegm, tightness in the chest, and low physical tolerance to exercise. Bronchoconstriction is also imminent.
Diagnosis of chronic obstructive asthma may entail a thorough medical history, physical examination, specific lung function tests, bronchodilator response test, peak expiratory flow (PEF) monitoring, imaging, allergy testing, and induced sputum testing among others. Treatment may involve bronchodilators, anti-inflammatory medications, and a few lifestyle modifications depending on the predominant symptoms and underlying factors.
How to Distinguish Chronic Obstructive Asthma from Other Infections
Distinguish Chronic Obstructive Asthma from Asthma – Diagnosis
- Normal asthma often begins in childhood while chronic obstructive asthma often sets off in adulthood.
- Chronic obstructive asthma has more persistent signs and symptoms than normal asthma, whose symptoms are intermittent.
- Asthma tends to show reversible airflow limitation on lung function tests opposed to chronic obstructive asthma with less reversibility and a fixed airflow limitation.
Distinguish Chronic Obstructive Asthma from Chronic Bronchitis – Diagnosis
This is an airway problem often associated with inflammation of the bronchi.
Chronic bronchitis can be caused by a genetic condition called alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
Distinguish Chronic Obstructive Asthma from Emphysema – Diagnosis
This refers to the pathological enlargement of airspaces distal to terminal bronchioles causing difficulty in breathing.
- Pulmonary function tests in chronic obstructive asthma show reversible air limitation while in emphysema, they show irreversible airflow limitation.
Distinguish Chronic Obstructive Asthma from Bronchiectasis – Diagnosis
This refers to irreversible widening or thickening of portions of the bronchi resulting from damaging the airway wall or inflammation.
Diagnosis of bronchiectasis may involve imaging studies like CT scans.
Distinguish Chronic Obstructive Asthma from Cystic Fibrosis – Diagnosis
This is a condition caused by inheriting abnormal genes, causing certain glands to produce abnormally thick secretions causing tissue and organ damage, most likely in the digestive tract and lungs.
- Chronic obstructive asthma only affects the respiratory system while cystic fibrosis can also affect other organs or systems.
- Cystic fibrosis is a genetic condition while chronic obstructive asthma is not genetic.
- Diagnosis of cystic fibrosis involves genetic testing.
Important Red Flags with Chronic Obstructive Asthma
Chronic obstructive asthma presents with a lot of respiratory distress, as many other respiratory conditions do, therefore sometimes posing a problem with diagnosis. If not identified and well managed on time, it can cause adverse conditions and may sometimes lead to the death of a patient.
Some of the red flags include; frequent exacerbations, limited response to medication, and decline in lung function.
