Contents
- 1 Atherosclerotic Heart Disease Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How to Distinguish Atherosclerosis from Other Diseases
- 2.1 Distinguish Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease from Atherosclerosis – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Anxiety from Atherosclerosis – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Angina from Atherosclerosis – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish Pericarditis from Atherosclerosis – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Myocardial Infarction from Atherosclerosis – Diagnosis
- 2.6 Distinguish Pulmonary Embolism from Atherosclerosis – Diagnosis
- 2.7 Distinguish Aortic Dissection from Atherosclerosis – Diagnosis
- 3 Atherosclerosis Red Flags and Management
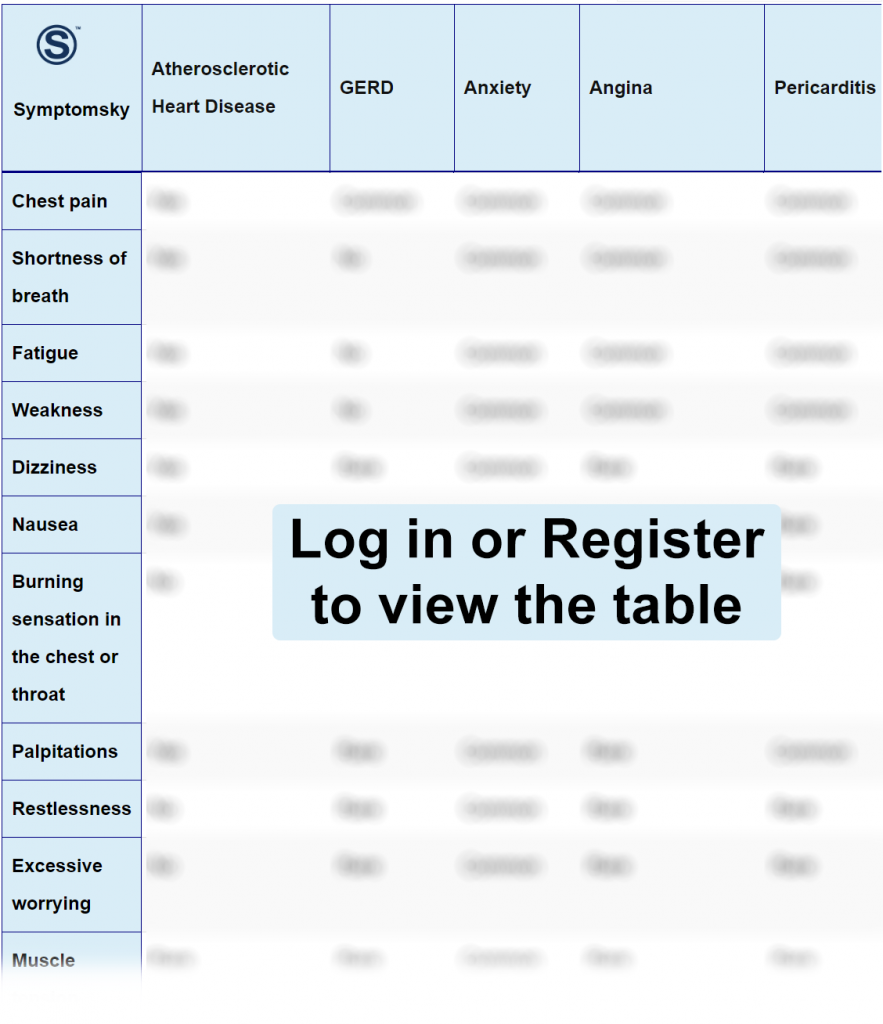
Atherosclerotic Heart Disease Differential Diagnosis Table:
Atherosclerosis is a progressive inflammatory disease. It is defined as narrowing or hardening of arteries due to the deposition of plaque in arteries, leading to a decrease in the oxygen supply to vital organs. Symptoms experienced include dizziness, extreme fatigue, heart palpitations, dyspnea, nausea, and chest pain. Tests for diagnosis, such as biomarkers like C-reactive proteins, LDL, HDL, triglycerides, and cholesterol levels, are reliable. Also, imaging such as ultrasound, EKG, and ECG.
How to Distinguish Atherosclerosis from Other Diseases
Distinguish Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease from Atherosclerosis – Diagnosis
Gastro-esophageal reflux disease is a chronic inflammatory digestive disease of the stomach that causes acid to reflux.
- Gastro-esophageal reflux disease is accompanied by heartburn after eating that intensifies at night, but atherosclerosis is not associated with food or time.
- Gastro-esophageal reflux disease has throat pain and chronic cough, both are absent in atherosclerosis.
“Esophageal pH monitor and Upper GI endoscopy are used for differentiation.”
Distinguish Anxiety from Atherosclerosis – Diagnosis
Anxiety is a psychological disorder of constant worrying, fearing, and panicking, also can be physiological symptoms as restlessness, fatigue, dizziness, etc.
- Anxiety is associated with excessive worrying and restlessness, while atherosclerosis is not associated with excessive worrying and restlessness.
“Somatic and behavioral symptoms, in addition to psychosocial stress and difficulties evaluation are used for differentiation.“
Distinguish Angina from Atherosclerosis – Diagnosis
Angina is an atherosclerotic complication leading to partial or complete obstruction of coronary artery.
- Angina is characterized by sudden chest pain, squeezing and tightness, but sudden chest pain and tightness are absent in atherosclerosis.
“ECG and Coronary angiography are used for differentiation.”
Distinguish Pericarditis from Atherosclerosis – Diagnosis
Pericarditis is an inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart.
- Pericarditis has positive auscultation (the sound of pericardial friction rub), but Atherosclerosis has negative auscultation.
“ECG, CT, and Cardiac MRI are used for differentiation.”.
Distinguish Myocardial Infarction from Atherosclerosis – Diagnosis
Myocardial infarction is a partial or complete blockage of blood supply to the cardiac muscle.
- Myocardial infarction is characterized by sudden severe pain radiating to the left shoulder, arms, and neck, but atherosclerosis is not associated with sudden radiating pain.
“ECG, Cardiac MRI, and Biomarkers (cardiac troponins and creatine kinase) are used for differentiation.”.
Distinguish Pulmonary Embolism from Atherosclerosis – Diagnosis
- Pulmonary embolism is a disruption in the pulmonary artery blood flow.
- Pulmonary Embolism includes hemoptysis (coughing blood-containing secretions), which is absent in atherosclerosis.
“Pulmonary angiography, CTPA (computed tomographic pulmonary angiography), and V/Q scan are considered the golden standard for differentiation.”.
Distinguish Aortic Dissection from Atherosclerosis – Diagnosis
Aortic Dissection is dysfunction in the aortic artery causing a tear in its lining.
- Aortic Dissection is felt as sudden severe pain radiating to the back described as a tearing sensation, unlike atherosclerosis, which is not accompanied by sudden pain radiating to the back
- Aortic dissection is characterized by an imbalance between upper extremities’ blood pressure. Yet, atherosclerosis is not associated with blood pressure imbalance.
“Transesophageal ECG, MR angiography, and CT angiography are used for differentiation.”.
Atherosclerosis Red Flags and Management
If Atherosclerosis left untreated, it can lead to sudden death and hemodynamic deterioration.
Atherosclerosis is managed by decreasing risk factors through comprehensive treatment, including lifestyle and pharmacological intervention. Lifestyle modifications include following a healthy diet, supervising body weight, increasing physical activity, stress management, smoking cessation, and limiting alcohol intake. Pharmacological interventions include cholesterol-lowering and anticoagulants.
