Contents
- 1 Acute Urticaria Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How To Distinguish Acute Urticaria From Other Diseases
- 2.1 Distinguish Contact Dermatitis from Acute Urticaria – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Exanthematous Drug Eruption from Acute Urticaria – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Scabies from Acute Urticaria – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish Systemic Lupus Erythematosus from Acute Urticaria – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish Angioedema from Acute Urticaria – Diagnosis
- 2.6 Distinguish Erythema Multiforme from Acute Urticaria – Diagnosis
- 2.7 Distinguish Prurigo Nodularis from Acute Urticaria – Diagnosis
- 2.8 Distinguish Dermatographism from Acute Urticaria – Diagnosis
- 3 Prevention from Acute Urticaria
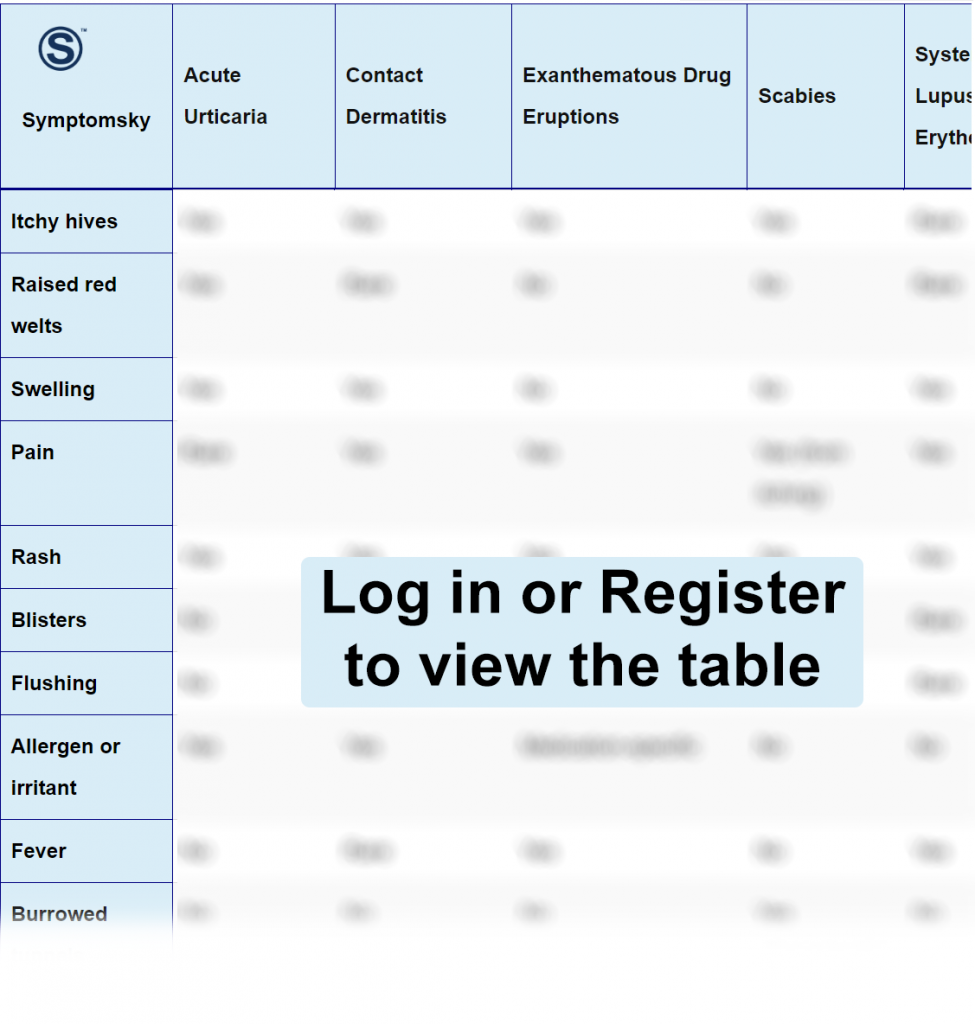
Acute Urticaria Differential Diagnosis Table:
Acute urticaria or Hives is a vascular reaction in which smooth, erythematous, slightly raised plaques or papules are formed on the skin that become itchy and last not longer than 6 weeks. It can present with wheals, angioedema, or both. Factors that cause acute urticaria include; allergic reactions to certain foods, soaps, and drugs, local irritants, shellfish, plant pollens, latex, stress, environmental factors, and insect bites or stings.
Symptoms of acute urticaria are; red or skin-colored, raised, itchy welts or bumps, hives which turn white (blanch) when pressed from the center, angioedema, sometimes painful swelling on eyes, lips, and throat.
Acute urticaria can simply be diagnosed based on the patient’s history and clinical examination and a skin prick test. If there is a suspicion of food or drug allergy, then radioallergosorbent tests (RAST) or CAP flour immunoassay can also be performed. Anti-histamines, anti-inflammatory, and anti-itch lotions can be used to relieve the symptoms.
How To Distinguish Acute Urticaria From Other Diseases
Distinguish Contact Dermatitis from Acute Urticaria – Diagnosis
Contact Dermatitis is a type of eczema in which there is an itchy rash caused by contact with an allergen or some irritant in your environment. The features which differentiate contact dermatitis from acute urticaria are;
- Contact dermatitis shows an allergic reaction hours to days after contact with the causative agent while acute urticaria is an immediate reaction.
- In Contact dermatitis, the skin becomes dry, itchy, blistered, and cracked while in urticaria there are wheals, hives, raised lesions, and blanching.
- There is pain in patients with contact dermatitis while in acute urticaria, it is unlikely to have pain.
Contact dermatitis is diagnosed based on history and examination; a patch test can also be performed. It usually goes away when the factor causing it is removed. To help with symptoms, anti-itch creams can be used.
Distinguish Exanthematous Drug Eruption from Acute Urticaria – Diagnosis
Exanthematous or Morbilliform Drug Eruption is a miscellaneous group of skin reactions occurring after exposure to a certain variety of drugs. It resembles pruritic and eczematous skin lesions. The features that differentiate exanthematous drug eruption from acute urticaria are;
- It is caused by only certain drugs such as antibiotics while acute urticaria, in addition to drugs, has other causative agents like irritants, food, environmental factors, and stress.
- Exanthematous Drug Eruption is a drug-induced reaction while Acute Urticaria is a type 1 hypersensitivity reaction.
- The rash in exanthematous drug eruption arises on the trunk then spreads symmetrically to the proximal extremities while acute urticaria doesn’t show such a pattern.
- Symptoms include erythema, mucous membrane erosions, blisters, palpable purpura, skin necrosis while acute urtica has hives, wheals with no blisters.
It is diagnosed based on history and clinical examination. Skin intradermal/prick tests and patch tests can also be performed.
Distinguish Scabies from Acute Urticaria – Diagnosis
Scabies is a contagious skin rash caused by a parasite called Sarcoptes scabiei. Itchy rash and severe itching are the two main symptoms. The features that distinguish scabies from acute urticaria are;
- Scabies causes intense itching, usually on private parts and finger webs, and mostly at night, while urticaria can appear anywhere and anytime of the day.
- Scabies mites make burrows into the skin; they live and lay eggs in burrows while acute urticaria is caused by direct contact with the causative agent.
- Scabies spreads through person-to-person contact and contact with infected belongings while acute urticaria doesn’t spread through physical contact.
- Scabies rash takes 2 to 6 weeks to appear after contact with scabies mite while Acute urticaria shows an immediate response after contact with an irritant.
Scabies is usually diagnosed based on history and examination, but microscopic examination of skin scrapping of burrows can also be done. Itching can persist for 2 to 4 weeks after successful treatment.
Distinguish Systemic Lupus Erythematosus from Acute Urticaria – Diagnosis
SLE is a long-lasting autoimmune disease that affects many organs or organ systems, although it mostly affects the skin, blood cells, kidneys, nervous system, and joints. The features that differentiate SLE from acute urticaria are;
- Symptoms of SLE include fever, myalgias, arthralgias, malaise, joint pains, headache, and loss of appetite while acute urticaria is unlikely to show these symptoms.
- SLE shows a butterfly-shaped rash on the face while acute urticaria rash (weals) can form rings, round, giant patches, or a map-like pattern.
- SLE is an autoimmune disease while Acute urticaria is caused by allergens and irritants.
SLE is diagnosed based on history, clinical examinations, blood and urine tests for ANA and Anti-Smith antibodies, and X-rays.
Distinguish Angioedema from Acute Urticaria – Diagnosis
Angioedema is a reaction that causes swelling of tissues in the deeper layer of the skin. It can cause swelling on the face, hands, feet, genitals, or sometimes the throat. The features that distinguish Angioedema from acute Urticaria;
- Angioedema is swelling in the deeper layer of dermis and subcutaneous tissue while acute angioedema develops swelling on the surface.
- Angioedema is a localized area of soft tissue swelling while acute urticaria is discrete areas of swelling that can be pruritic.
- Angioedema doesn’t respond to adrenaline while acute urticaria shows a response to adrenaline.
Angioedema is diagnosed based on history and clinical examination. There is no single test available to identify the exact cause of angioedema, but blood tests and allergy tests can be performed to rule out the specific cause.
Distinguish Erythema Multiforme from Acute Urticaria – Diagnosis
Erythema multiforme is an acute, self-limiting, recurrent, immune-mediated, type 4 hypersensitivity reaction caused by an allergic reaction to an infection or some medicines. The features that distinguish erythema multiforme from acute urticaria are;
- Erythema multiforme shows ‘target lesions’ (flat and round dark circles with purple-grey centers), itching, joint pains, fever, fatigue, blisters, and muco-cutaneous involvement while Acute urticaria doesn’t exhibit these symptoms.
- Erythema multiforme and Acute urticaria rash can appear anywhere on the body, but the former is more prominent on fingers and toes.
- Erythema multiforme has a painful rash and blisters while acute urticaria has a painless rash.
Diagnosis is mostly clinical and doesn’t require further investigations. It usually resolves within 2 to 4 weeks without any treatment.
Distinguish Prurigo Nodularis from Acute Urticaria – Diagnosis
Prurigo Nodularis or Picker’s nodule is a chronic skin condition caused by continuous, excessive scratching of the skin that results in multiple, firm, hard, severely itching patches, plaques, and bumps. The features that differentiate prurigo nodularis from acute urticaria are;
- Both of these lesions can present with itch, but itching caused by prurigo nodularis is so intense that it interferes with daily activities and sleep.
- Prurigo nodularis lesions are mostly present on the extensor surface of extremities while Acute urticaria can be present anywhere on the body.
- Prurigo nodularis can cause extreme scratching on examination while acute urticaria doesn’t show scratching on the lesion.
Prurigo nodularis can be diagnosed on clinical examination, examination under the microscope, and biopsy. It is treated with anti-itch medication.
Distinguish Dermatographism from Acute Urticaria – Diagnosis
Dermatographism or skin writing is a condition in which light scratching, pressure, or rubbing the skin results in inflamed and raised marks or welts. The features that distinguish dermatographism from acute urticaria are;
- Dermatographism is a form of urticaria, but the former develops on pressure or scratching the skin while the latter results from contact with an irritant.
- Welts in dermatographism disappear within an hour while acute urticaria can last for two to six weeks.
- Dermatographism has been documented in people with thyroid problems, pregnancy, diabetes, and menopause while acute urticaria isn’t related to systemic diseases.
It is diagnosed on history and examination; rarely, skin biopsy can be performed. Treatment isn’t needed, but mild anti-histamines can be used.
Prevention from Acute Urticaria
Acute urticaria can be prevented by identification and prevention of triggers, avoiding certain foods like peanuts, eggs, and shellfish, avoiding stress, avoiding physical exertion, prevention from hot and cold exposure, identifying drugs causing them and avoiding them in the future can help with developing urticaria.
If you see any change in skin color, rash, redness, or raised lesion, immediately consult the doctor.
