Contents
- 1 Acute Bronchitis Differential Diagnosis Table:
- 2 How To Distinguish Acute Bronchitis from Other Diseases
- 2.1 Distinguish Influenza from Acute Bronchitis – Diagnosis
- 2.2 Distinguish Pneumonia from Acute Bronchitis – Diagnosis
- 2.3 Distinguish Asthma from Acute Bronchitis – Diagnosis
- 2.4 Distinguish COPD from Acute Bronchitis – Diagnosis
- 2.5 Distinguish GERD from Acute Bronchitis – Diagnosis
- 2.6 Distinguish Postnasal Drip from Acute Bronchitis – Diagnosis
- 2.7 Distinguish Bronchiectasis from Acute Bronchitis – Diagnosis
- 3 Common Red Flags With Acute Bronchitis
Acute Bronchitis Differential Diagnosis Table:
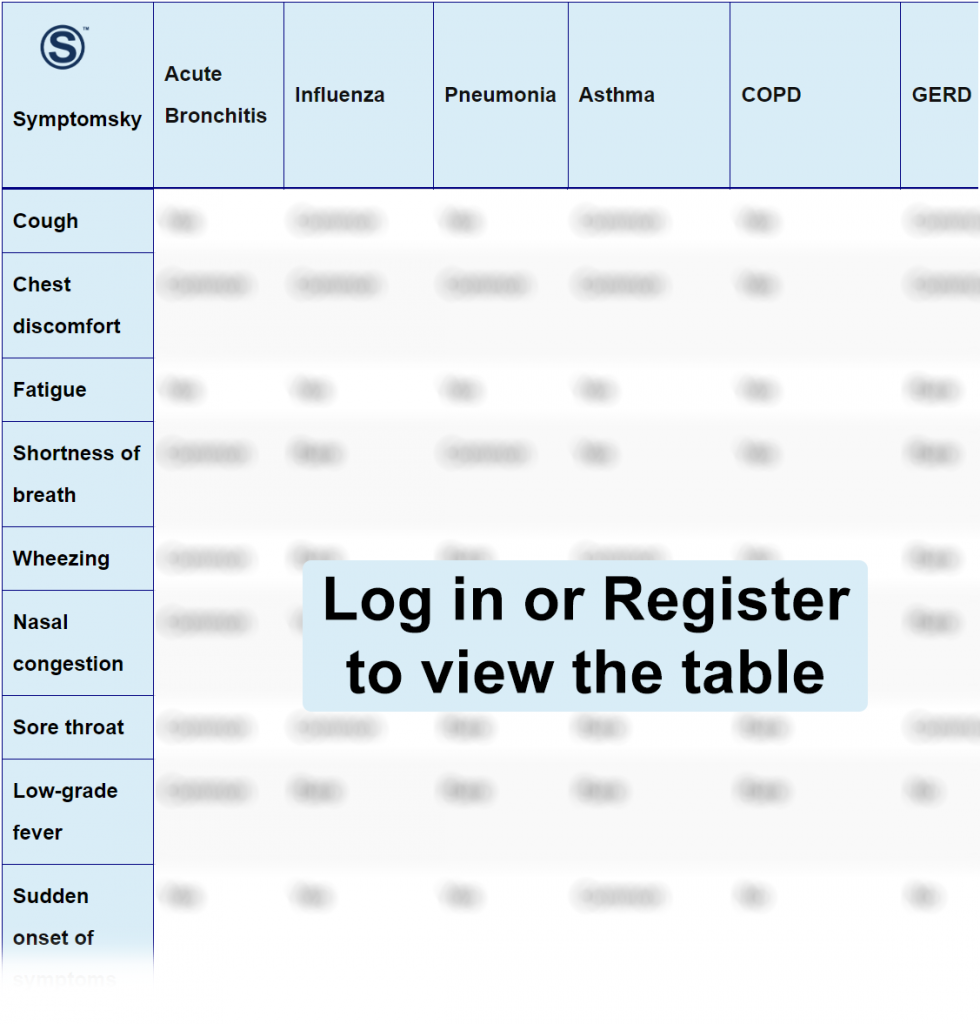
Acute Bronchitis is a short-term inflammation of the lungs’ bronchi. It’s a self-limiting disease that usually resolves in 7 to 10 days; but, in more serious cases, symptoms can persist for 3 weeks. The most common pathogen is a virus, but it can also be caused by other pathogens; therefore, the presentation of symptoms can vary. However, the most common presentation includes coughing, which is usually dry at first and then starts to produce mucus. This symptom typically lasts longer than the others. Other symptoms include low-grade fever, dehydration, fatigue, sore throat, nasal congestion, chest discomfort, dyspnea, wheezing, and tachycardia.
How To Distinguish Acute Bronchitis from Other Diseases
Distinguish Influenza from Acute Bronchitis – Diagnosis
Influenza, also known as flu, is an infection of the throat, nose, and throat caused by the influenza virus. It is a highly contagious respiratory infection and takes up to 10 days to heal.
- The presentation of both these diseases is very similar; both produce fatigue accompanied by cough and fever. However, Influenza normally produces high-grade fever, while acute bronchitis causes low-grade fever.
- Wheezing, a whistling sound while breathing, is a common manifestation of diseases like bronchitis and pneumonia, rare to be found in influenza.
- Moreover, flu symptoms usually appear suddenly, but bronchitis develops slowly, starting with a cough only.
Distinguish Pneumonia from Acute Bronchitis – Diagnosis
Pneumonia is an infection that makes the lungs’ alveoli inflamed; ultimately, they fill up with pus and fluid. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, so symptoms are highly variable as well.
- Pneumonia is actively involved in chest pain, which is not that common in bronchitis.
- Bronchitis, along with other symptoms, causes a sore throat as well. It is a rare finding in pneumonia patients.
Distinguish Asthma from Acute Bronchitis – Diagnosis
Asthma means shortness of breath. It is an inflammation of the airways that makes it difficult to breathe and produces symptoms like wheezing and coughing.
- Asthma is a chronic condition with episodes of acute attack. It means asthma normally stays for a longer duration like for months, while bronchitis heals within days or weeks.
- The common symptoms of bronchitis, like sore throat, fever, and nasal congestion, are not encountered in asthma frequently.
Distinguish COPD from Acute Bronchitis – Diagnosis
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic condition that obstructs the airflow of the lungs.
- COPD is a chronic disease, which means it stays for a longer duration, and the symptoms gradually develop over the period, while acute bronchitis stays for some days or a week, and symptoms have a sudden onset.
- Bronchitis is often accompanied by symptoms like sore throat, nasal congestion, and fever. These are not present in COPD.
- It is very rare to find chest pain in bronchitis while it’s fairly a common symptom of COPD.
Distinguish GERD from Acute Bronchitis – Diagnosis
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a condition caused by lower esophagus sphincter relaxation that leaks the acid back into the esophagus and irritates its lining.
- GERD is characterized by symptoms like acid reflux and regurgitation. These are never present in acute bronchitis.
- Symptoms of acute bronchitis, typically respiratory, such as wheezing and shortness of breath, are not seen in GERD.
- GERD can cause voice changes known as hoarseness, not seen in acute bronchitis.
Distinguish Postnasal Drip from Acute Bronchitis – Diagnosis
Postnasal drip is the accumulation of mucus at the back of the throat by dripping through the nose or sinuses.
- In postnasal drip, people constantly feel mucus in the throat, and there is an urge to clear the throat repeatedly. This symptom is not present in acute bronchitis.
- The common symptoms of acute bronchitis, like wheezing, chest discomfort, and shortness of breath, cannot be seen in postnasal drip patients.
- Excessive presence of mucus in the throat may cause nausea, not common in acute bronchitis.
Distinguish Bronchiectasis from Acute Bronchitis – Diagnosis
Bronchiectasis is a chronic pulmonary disease that leads to the widening of bronchial airways, leading to persistent cough, recurrent infections, and excessive mucus production.
- Bronchiectasis is a chronic infection with repeated respiratory infections and periods of symptom exacerbation. Acute bronchitis lasts only for a week.
- A common symptom among bronchiectasis patients is digit clubbing. It is not present in bronchitis patients.
- Another common sign is blood in the cough, which is rare in acute bronchitis cases.
Common Red Flags With Acute Bronchitis
Although acute bronchitis is not a life-threatening condition, it produces discomfort because of coughing. It should be kept in mind that frequent coughing can be a sign of more serious conditions. Cough that lasts for more than three weeks, high-grade fever for over multiple days, presence of blood in cough, confusion, and other pulmonary or cardiac conditions. Extensive coughing can be a sign of pulmonary emboli and lead to other conditions like pneumothorax.
